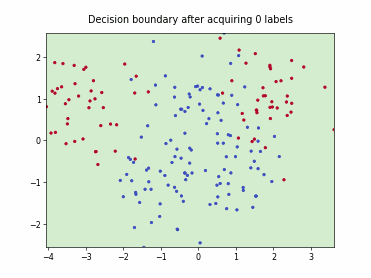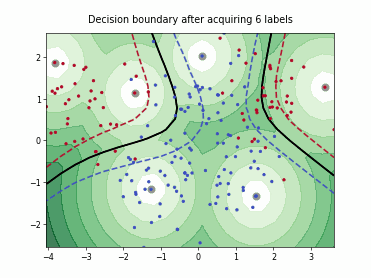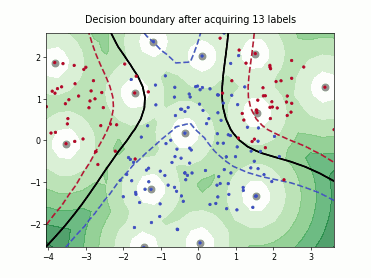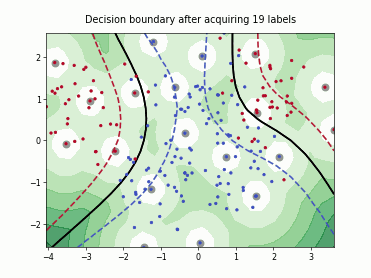
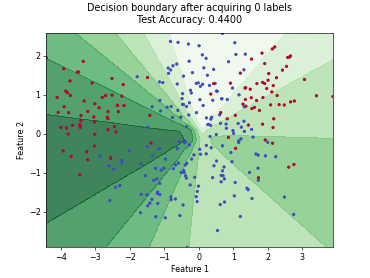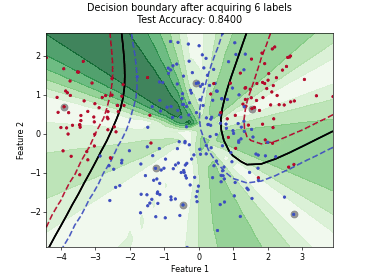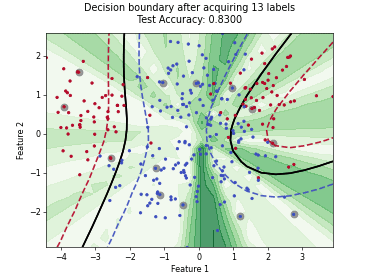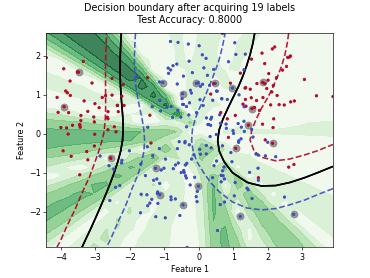
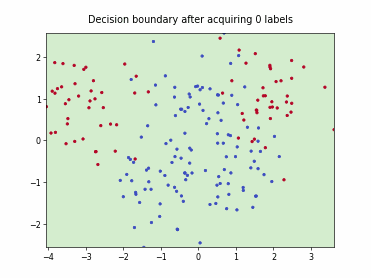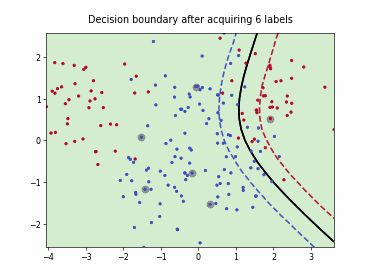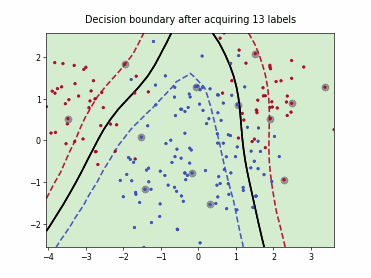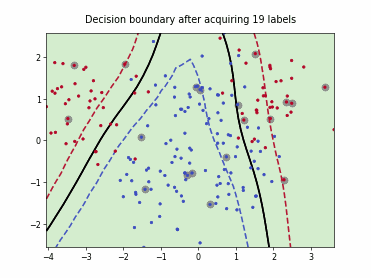
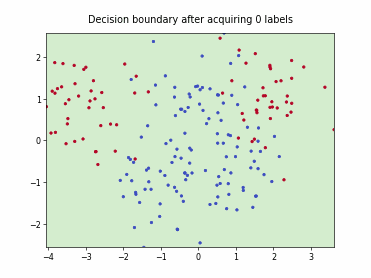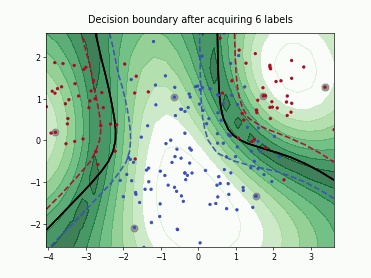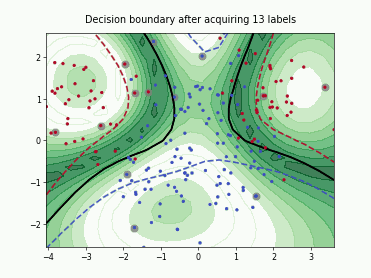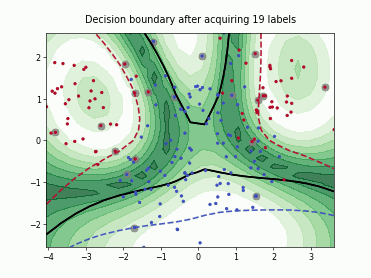
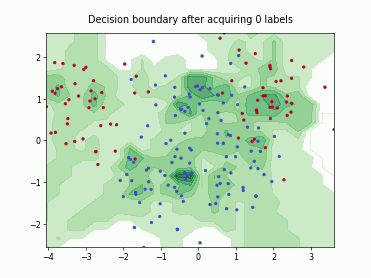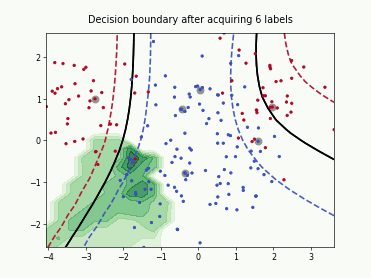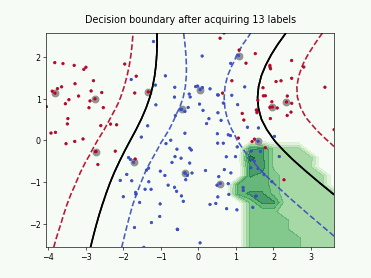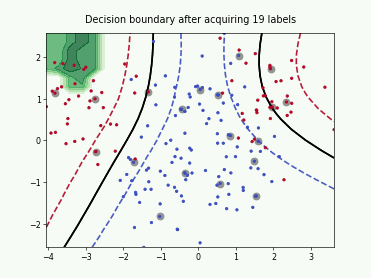
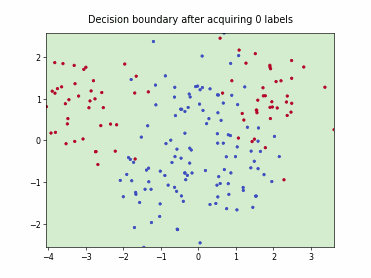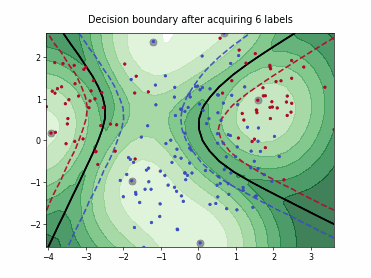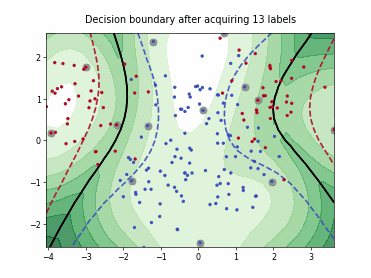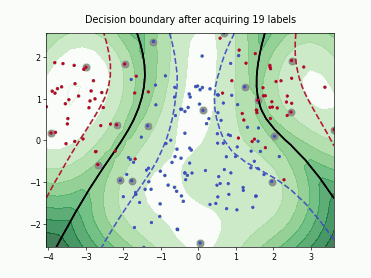
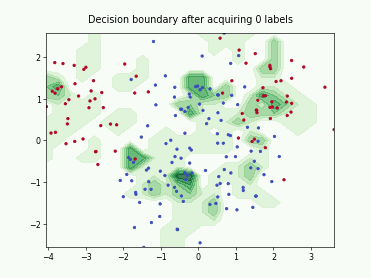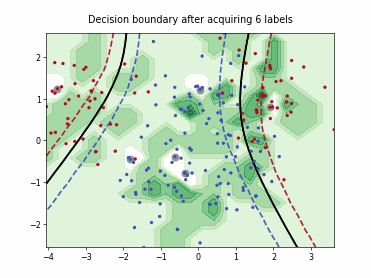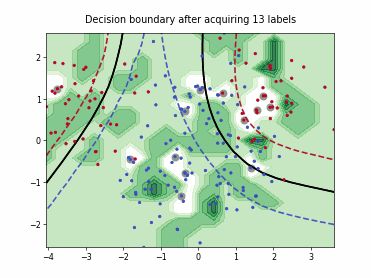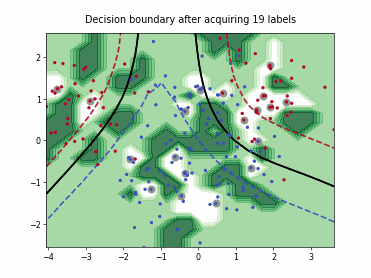
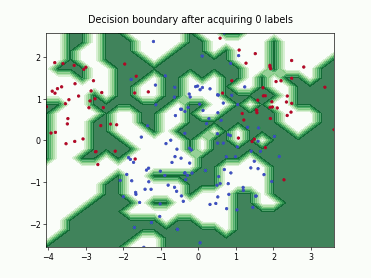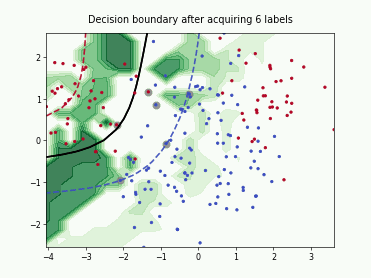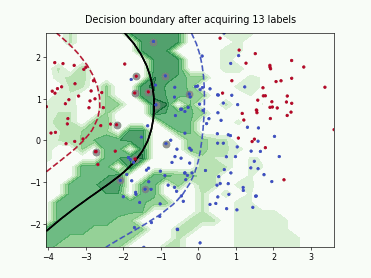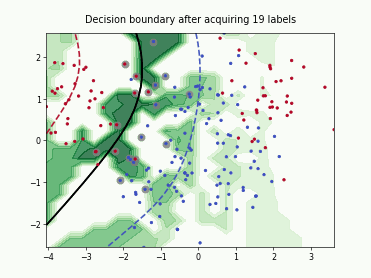
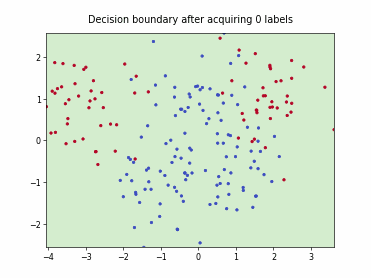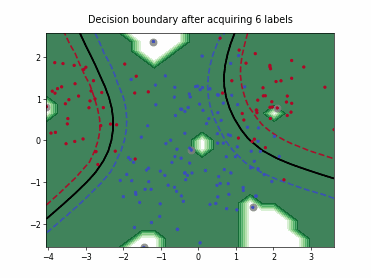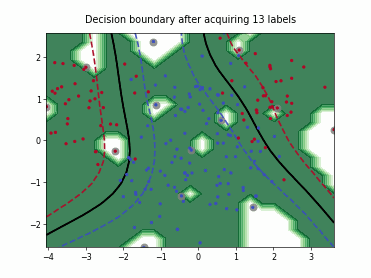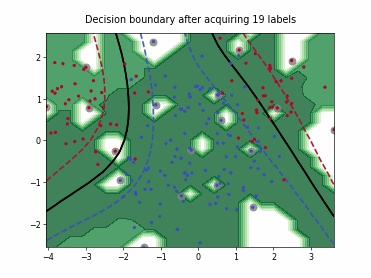
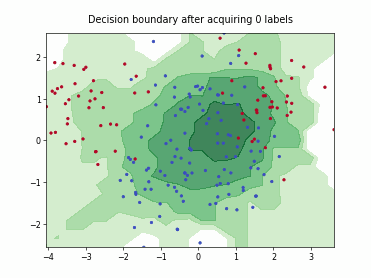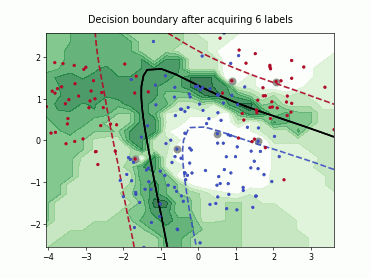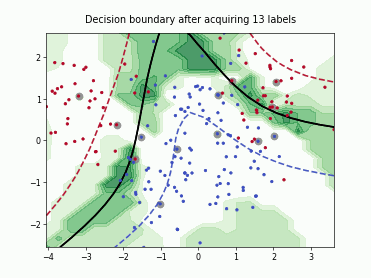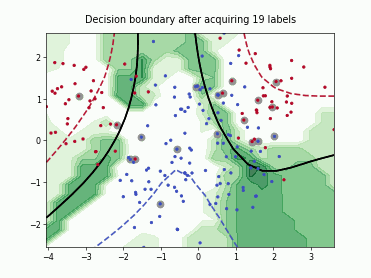
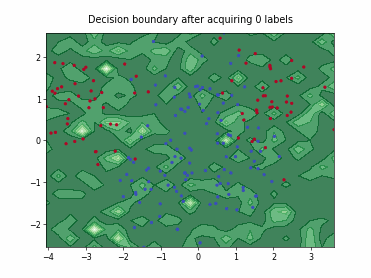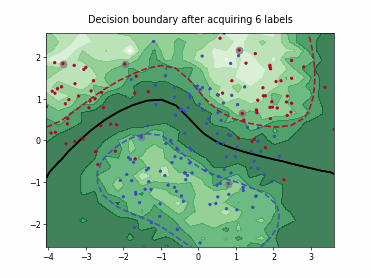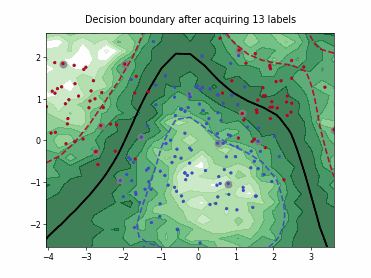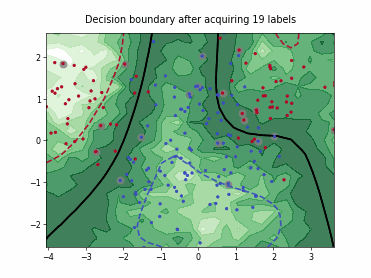
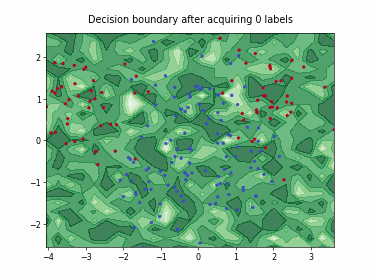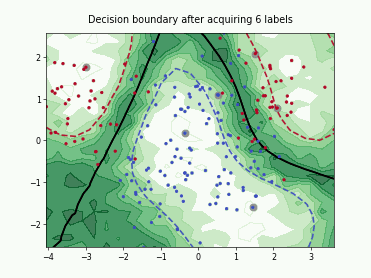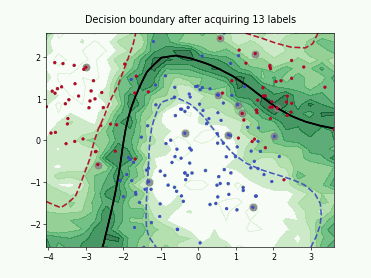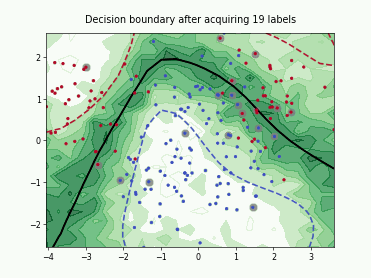
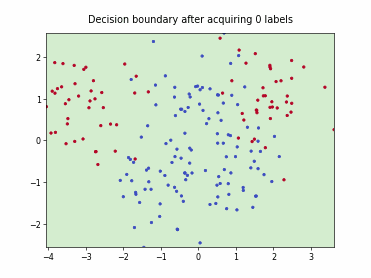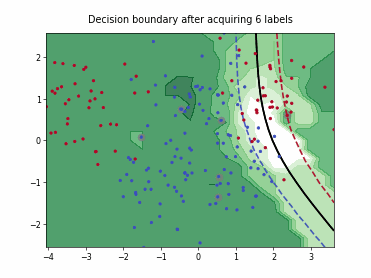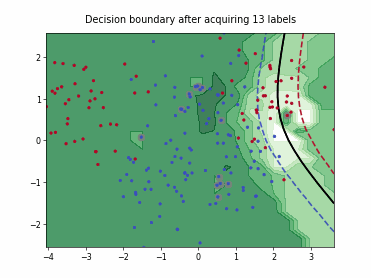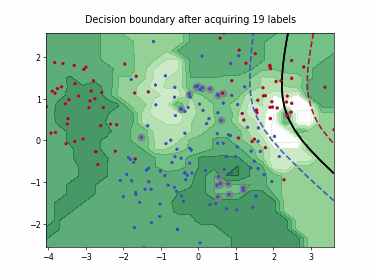
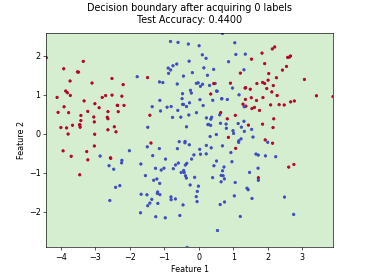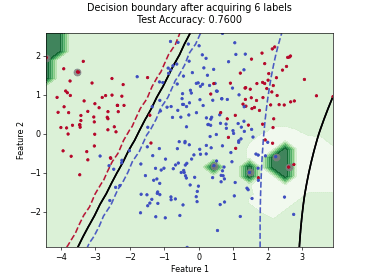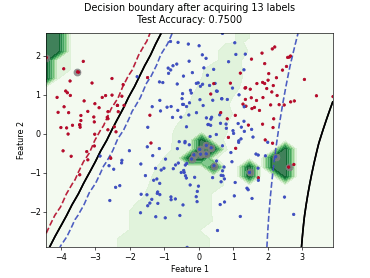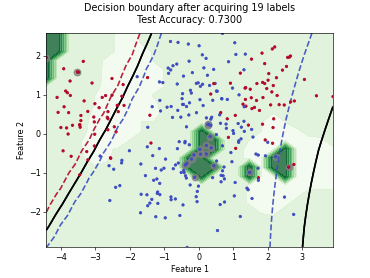
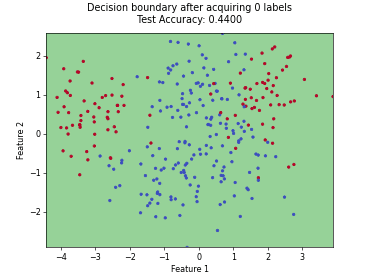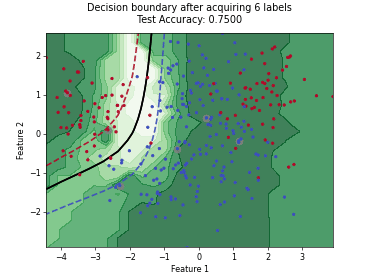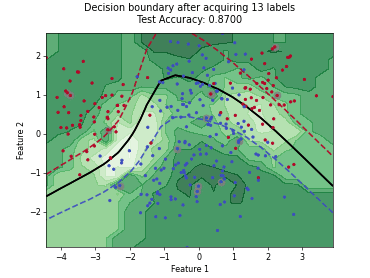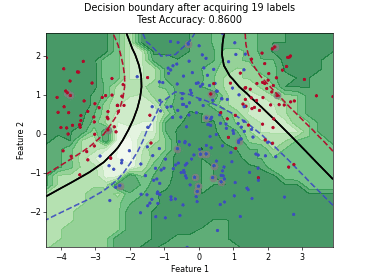
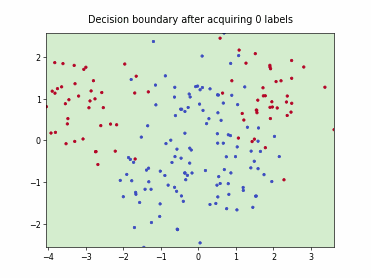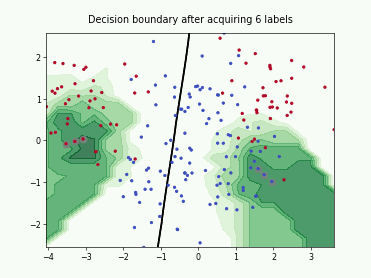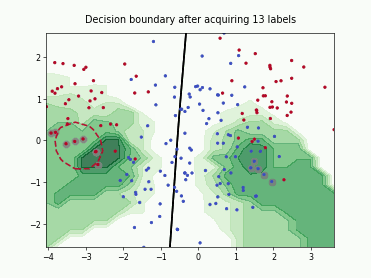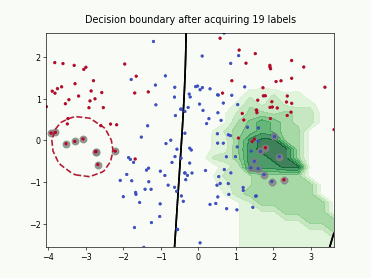
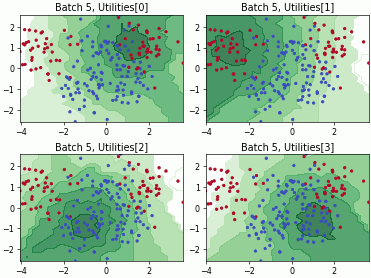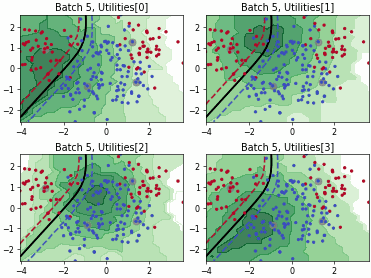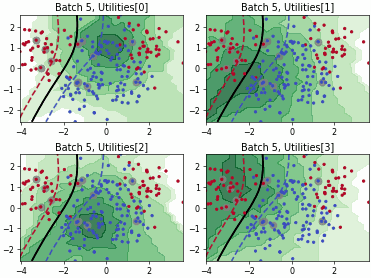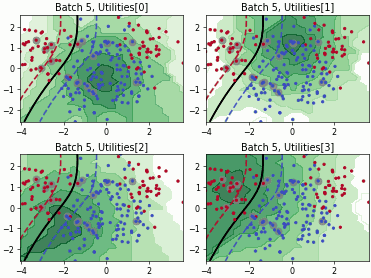
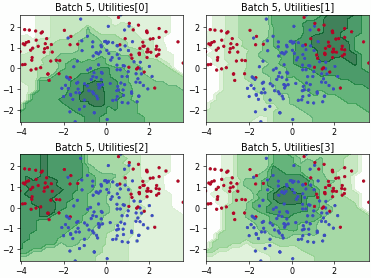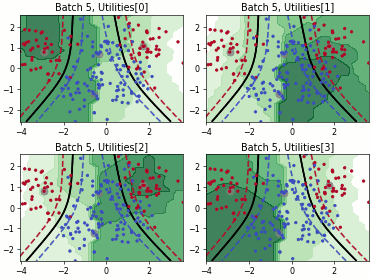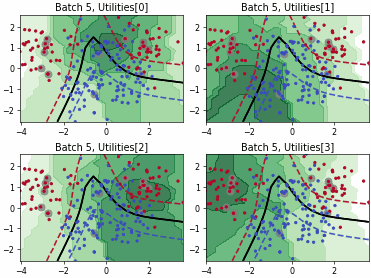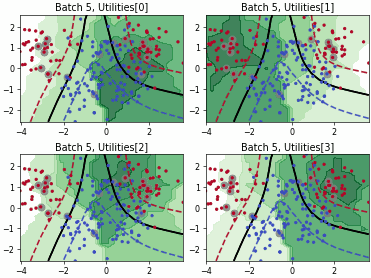
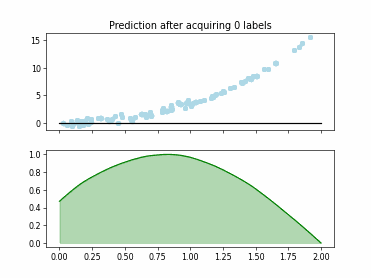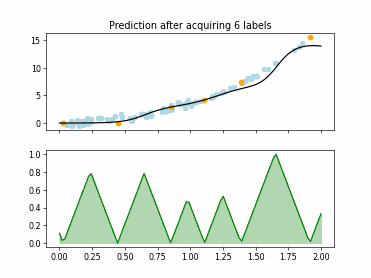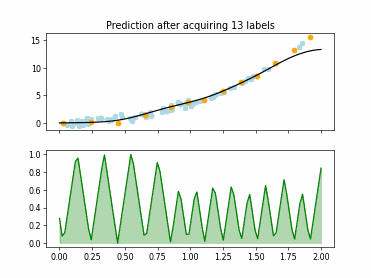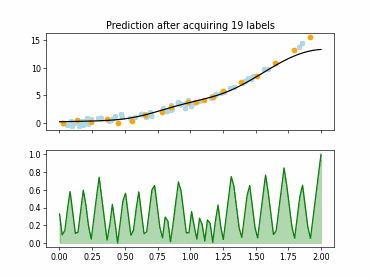
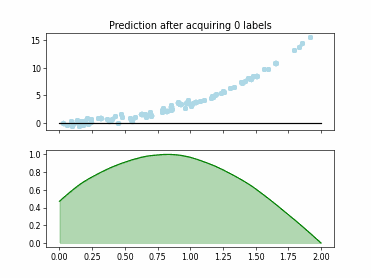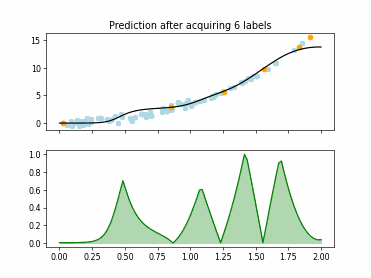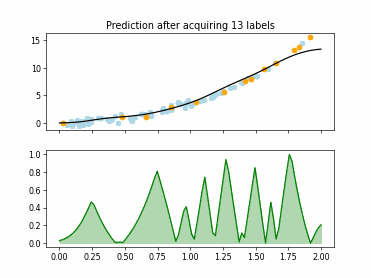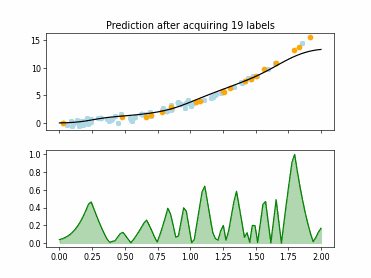
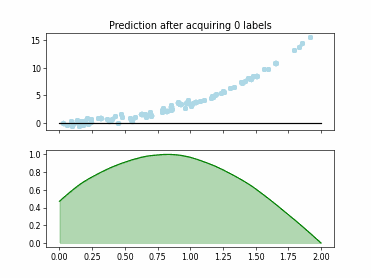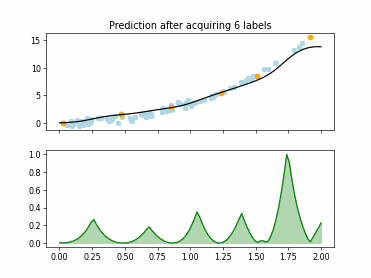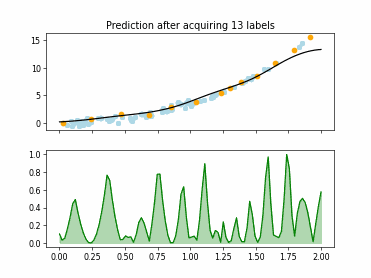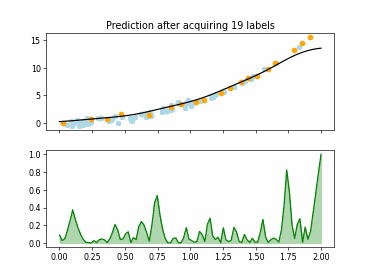
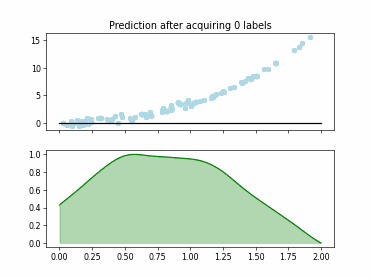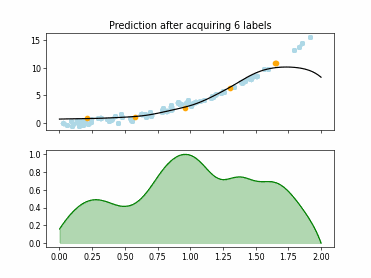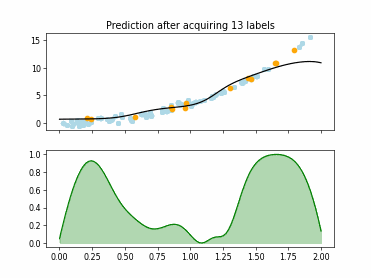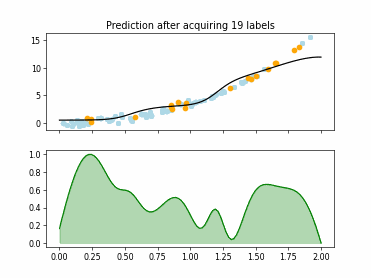
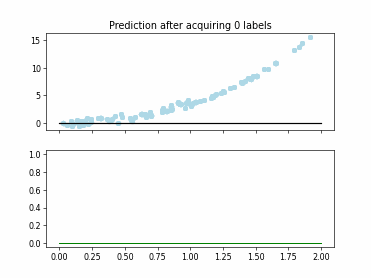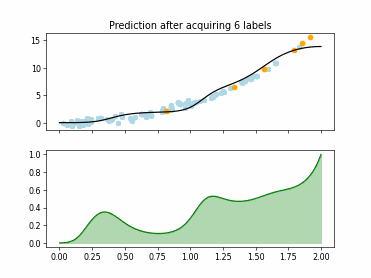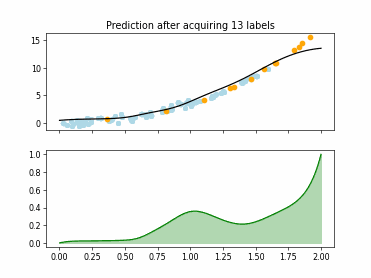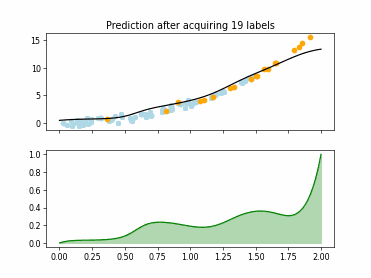
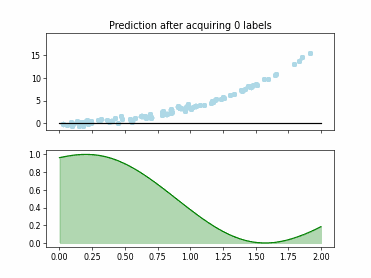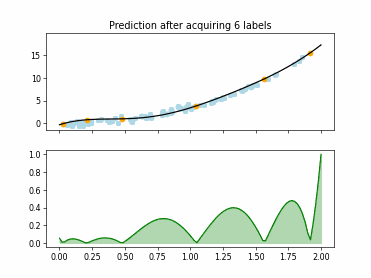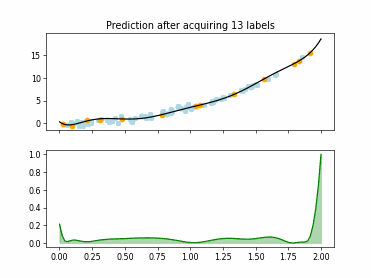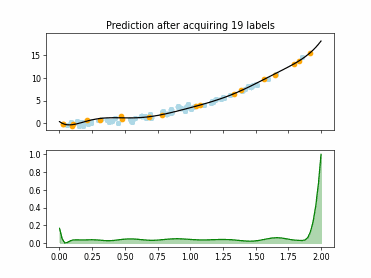
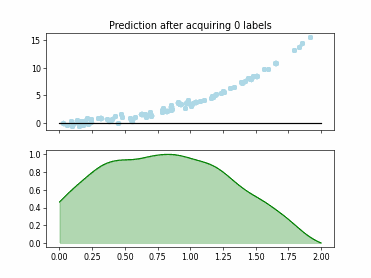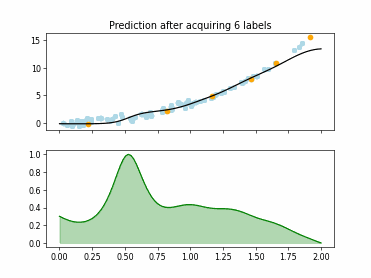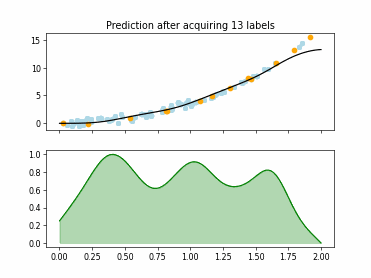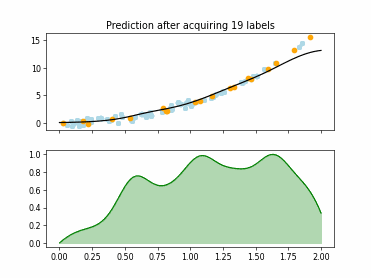
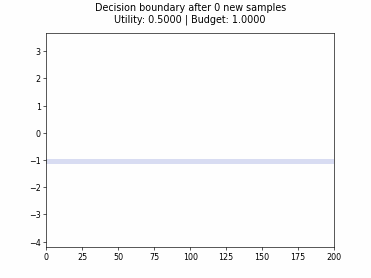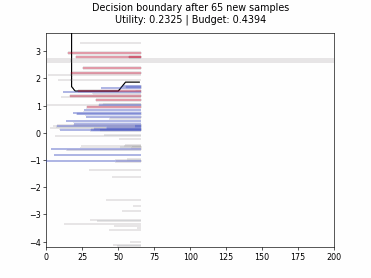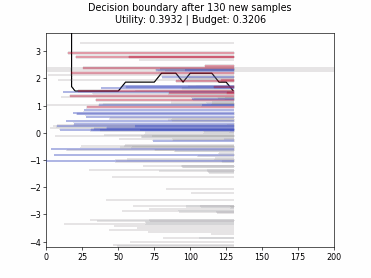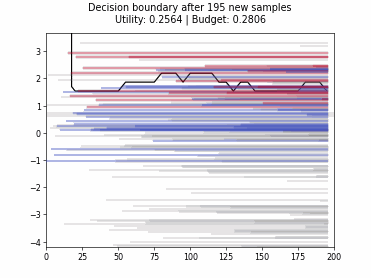
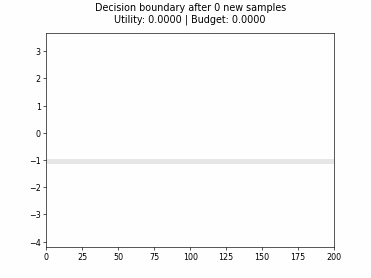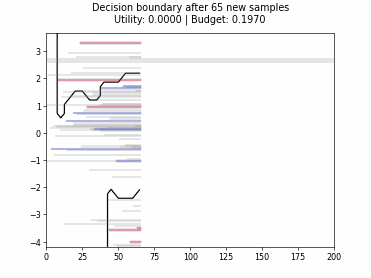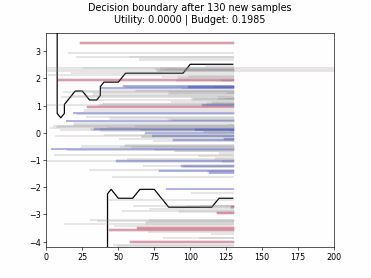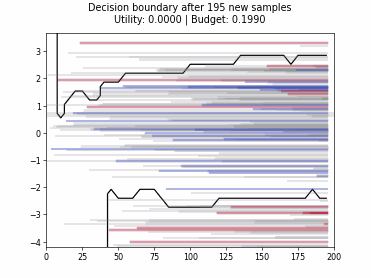
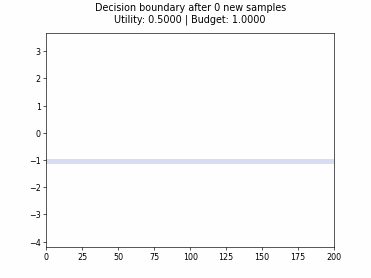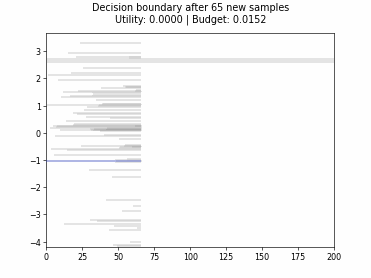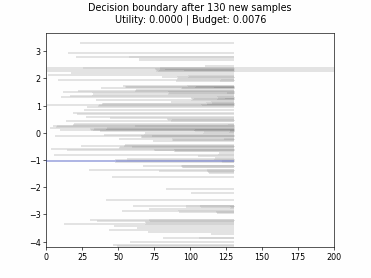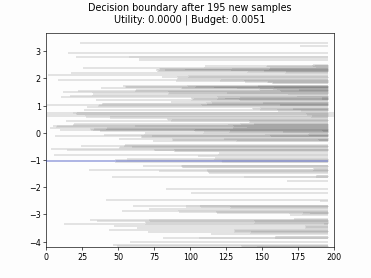
Visualizations#
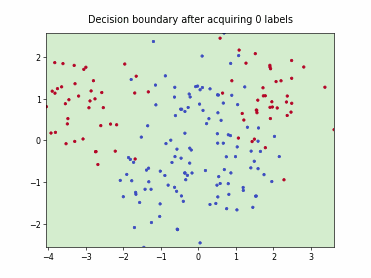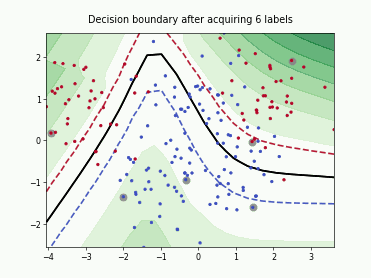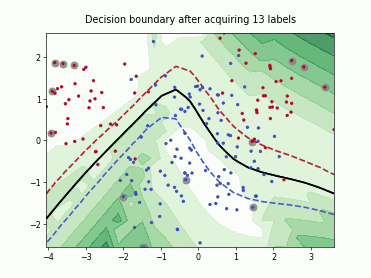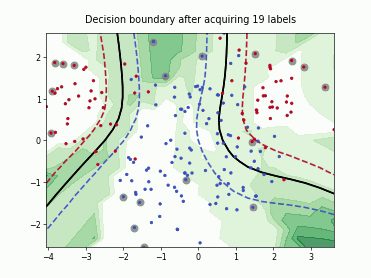
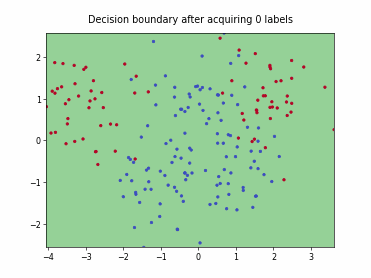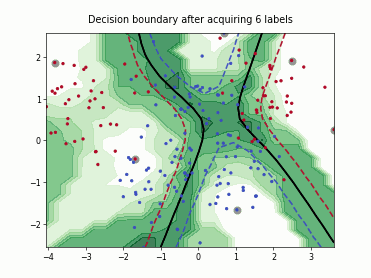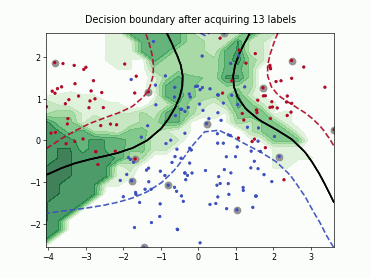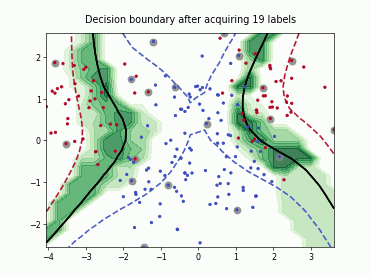
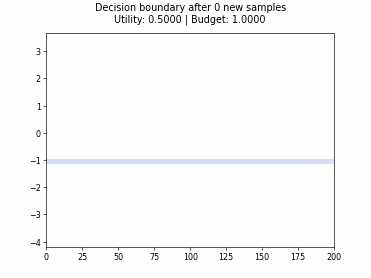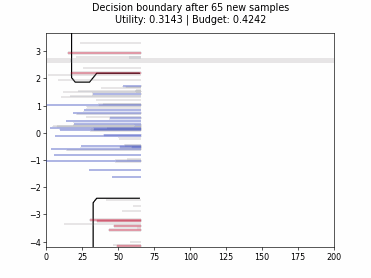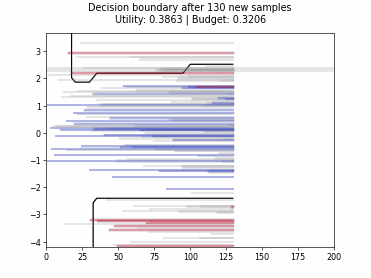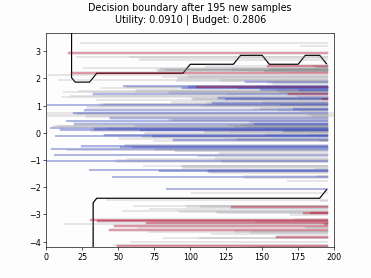
On this page, we illustrate how different query strategies behave across various active learning scenarios. To this end, we generate synthetic, low-dimensional toy datasets that allow us to visualize the distribution of samples selected for labeling in feature space. Each example consists of an animation and accompanying code that plot the results across individual active learning cycles.
Pool-based AL Strategies#

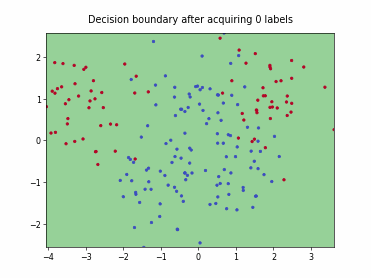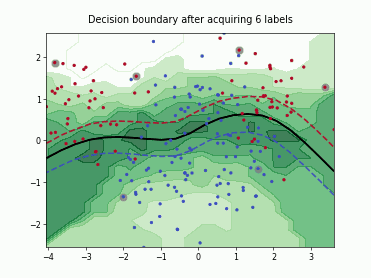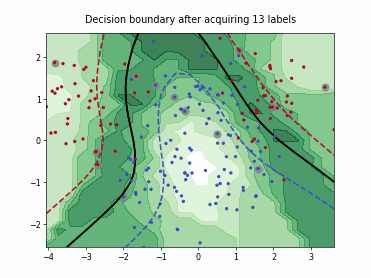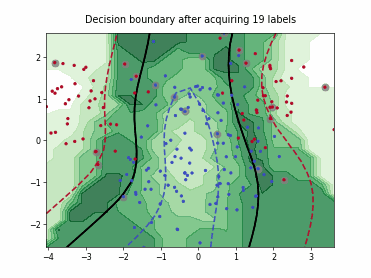
Querying Informative and Representative Examples (QUIRE)

Uncertainty Sampling with Expected Average Precision (USAP)
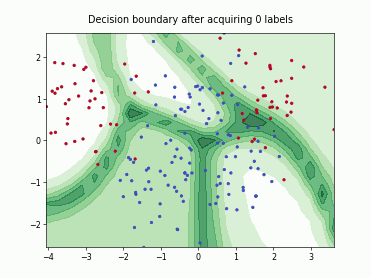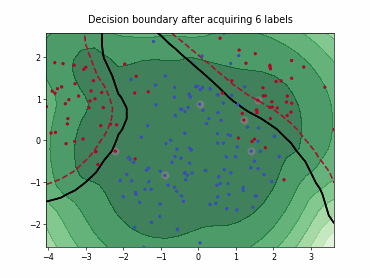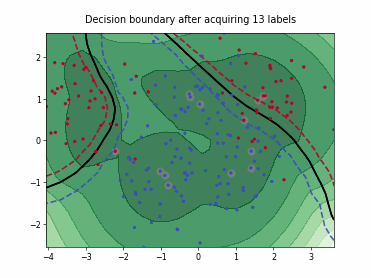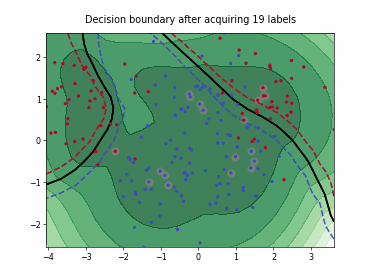
Density-Diversity-Distribution-Distance Sampling (4DS)
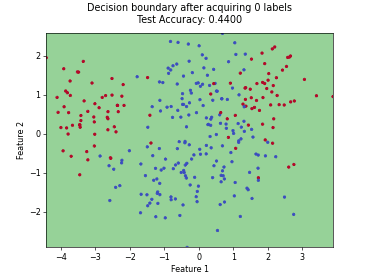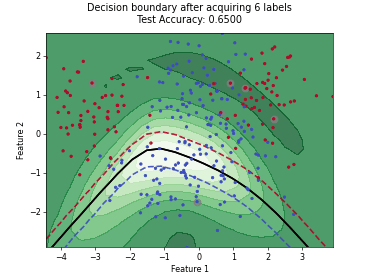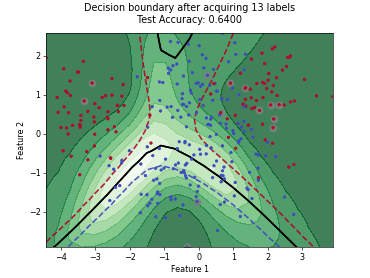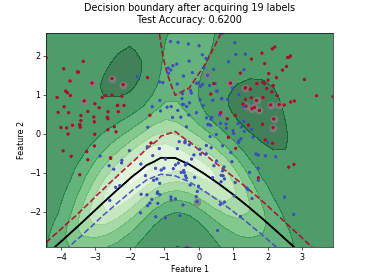
Monte-Carlo Expected Error Reduction (EER) with Log-Loss
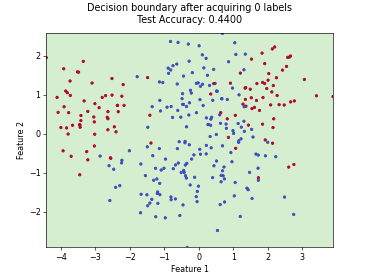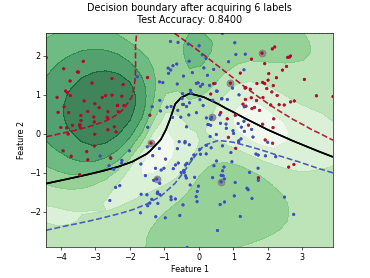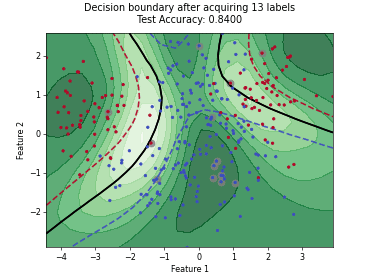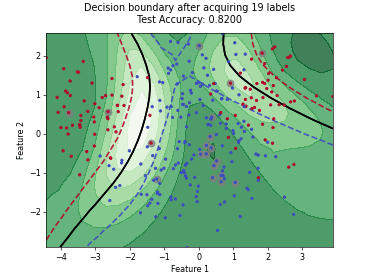
Monte-Carlo Expected Error Reduction (EER) with Misclassification-Loss
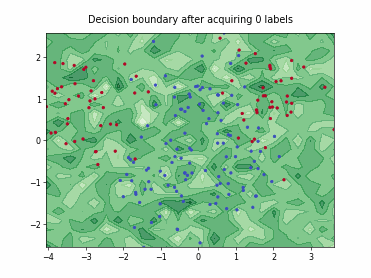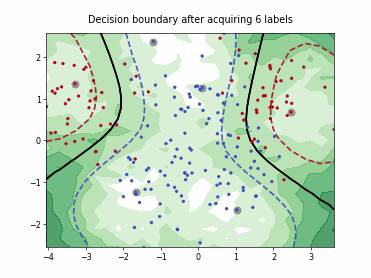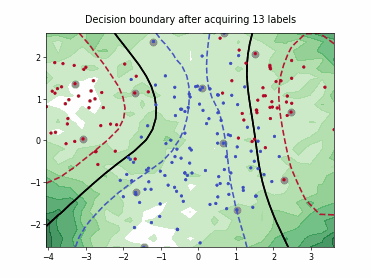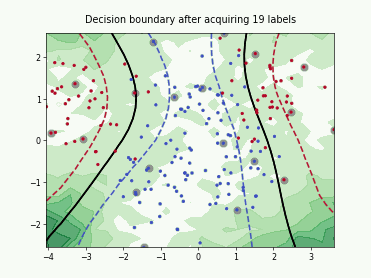
Query-by-Committee (QBC) with Kullback-Leibler Divergence
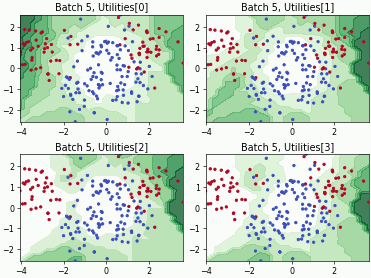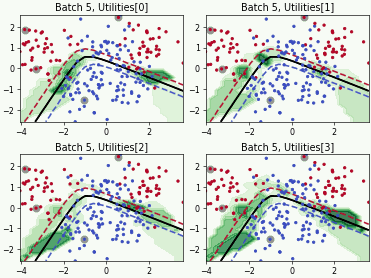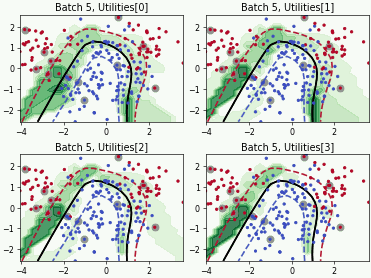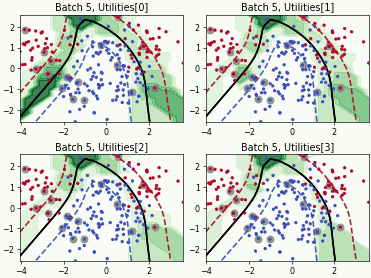
Batch Active Learning by Diverse Gradient Embedding (BADGE)
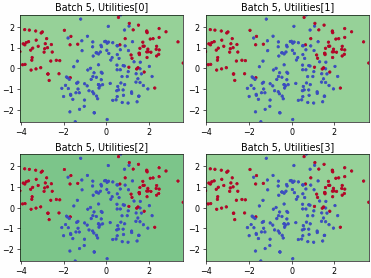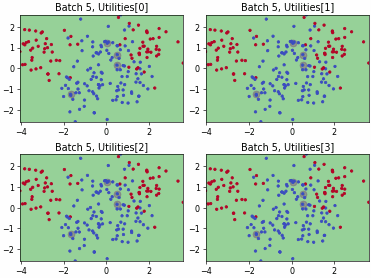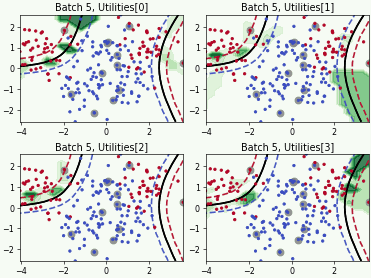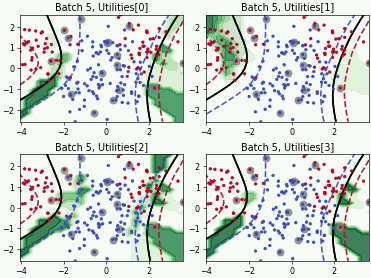
Fast Active Learning by Contrastive UNcertainty (FALCUN)
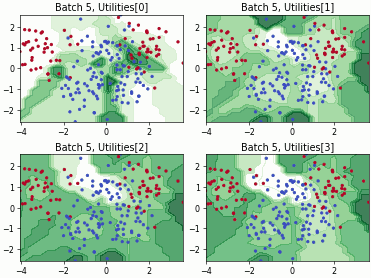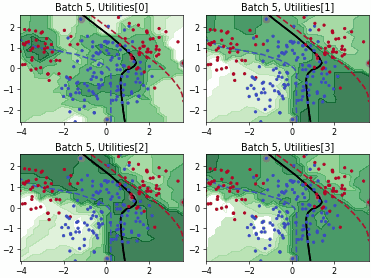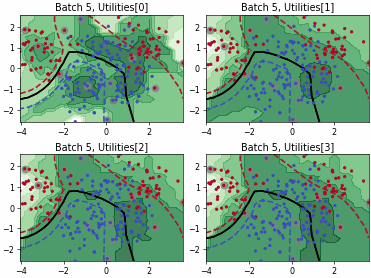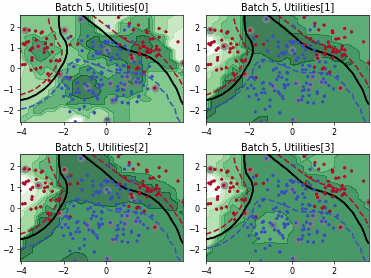
Batch Density-Diversity-Distribution-Distance Sampling (4DS)
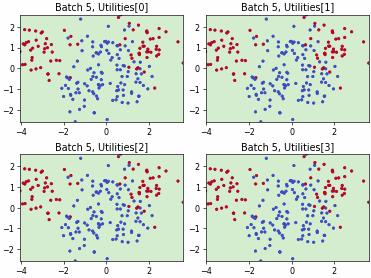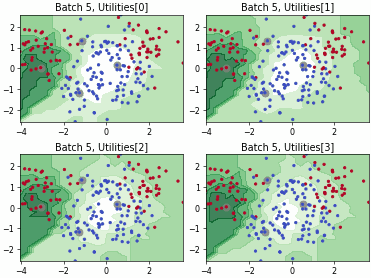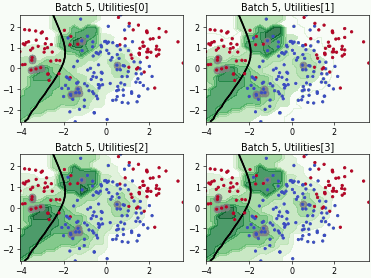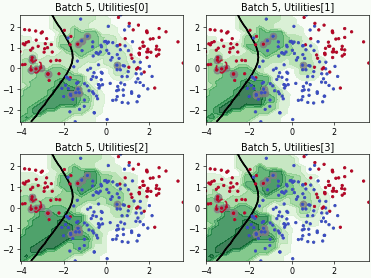
Batch Bayesian Active Learning by Disagreement (BatchBALD)
Pool-based AL Strategies for Regression#

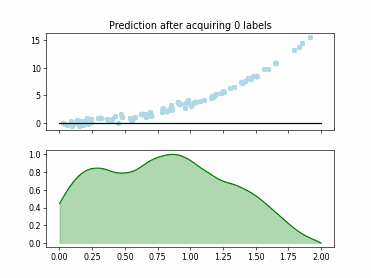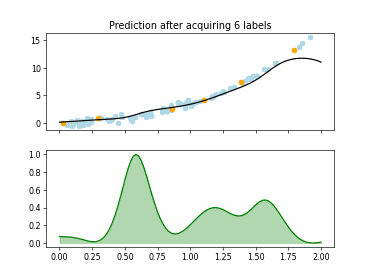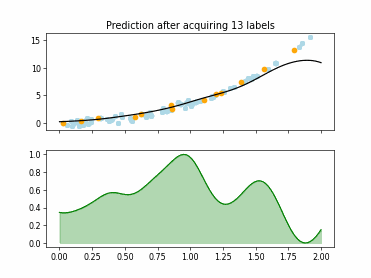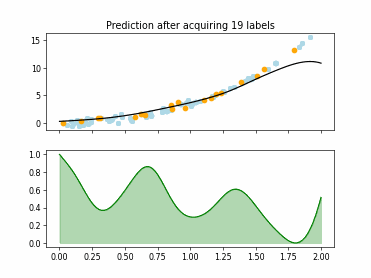
Regression based Kullback Leibler Divergence Maximization
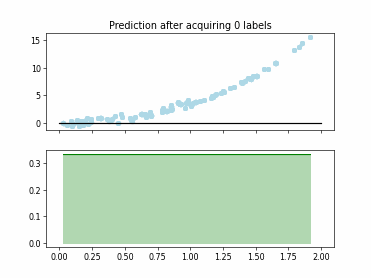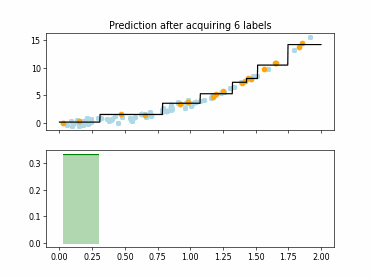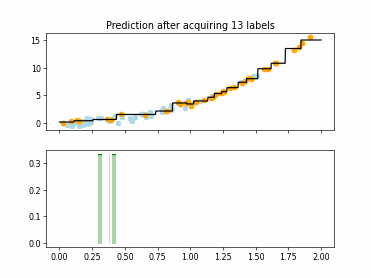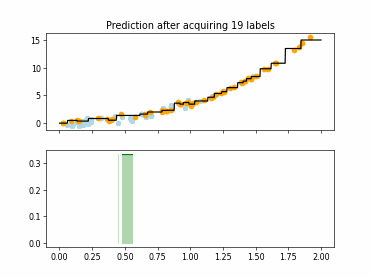
Regression Tree Based Active Learning (RT-AL) with Random Selection
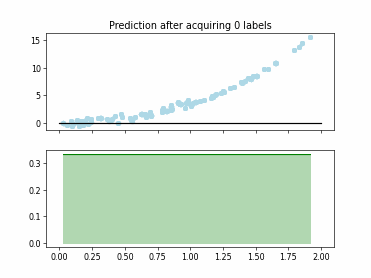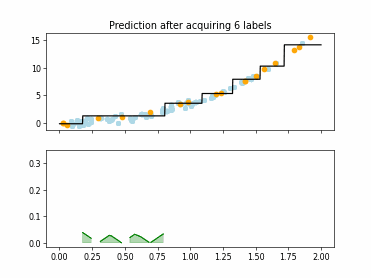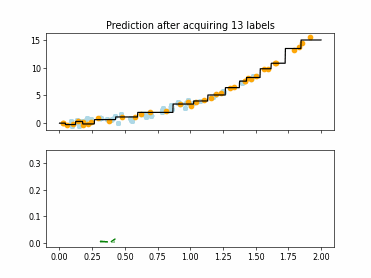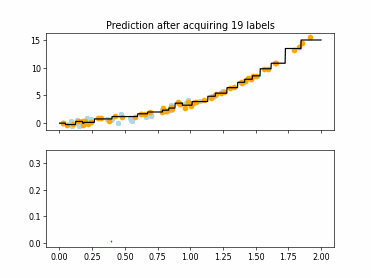
Regression Tree Based Active Learning (RT-AL) with Diversity Selection
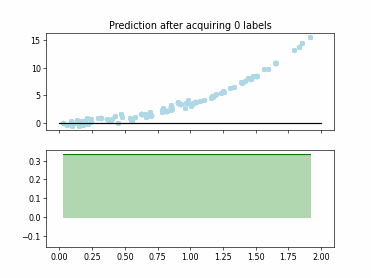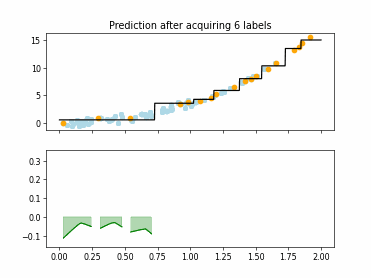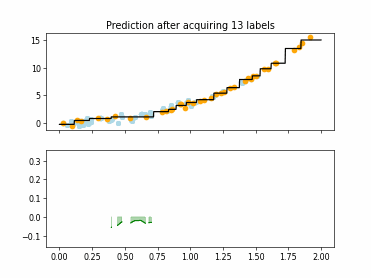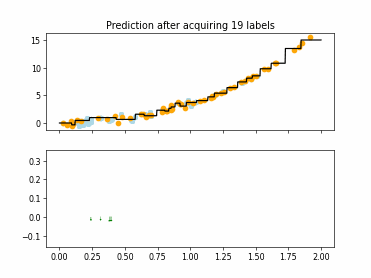
Regression Tree Based Active Learning (RT-AL) with Representativity Selection
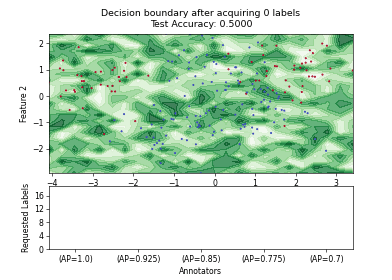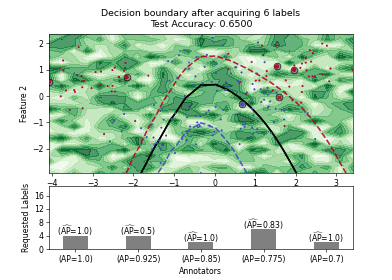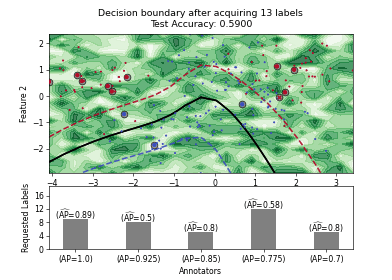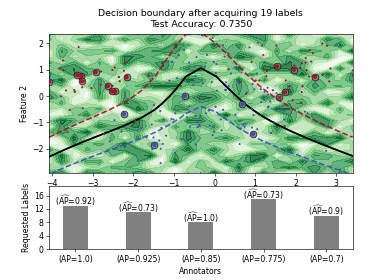
Pool-based AL Strategies for Mulitple Annotators#

Stream-based AL Strategies#

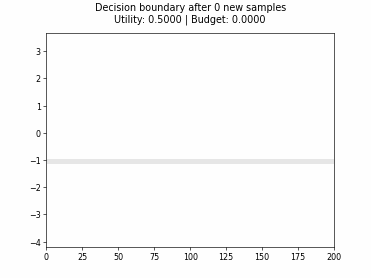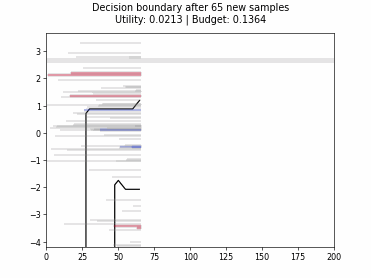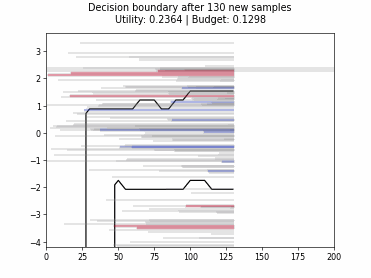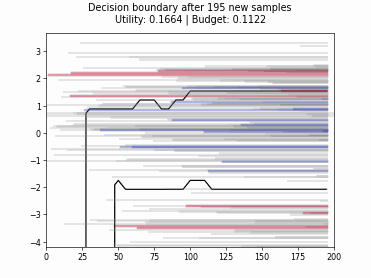
Cognitive Dual-Query Strategy with Random Sampling
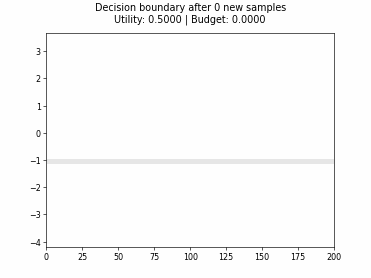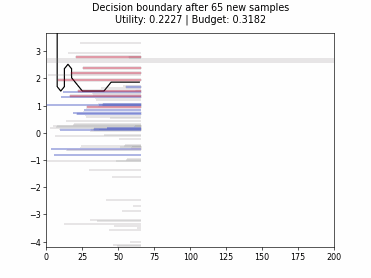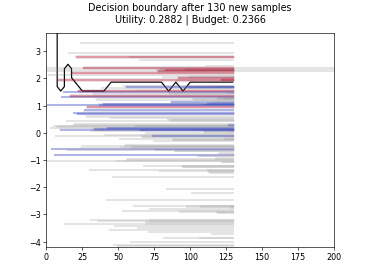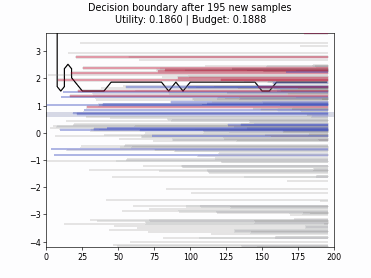
Cognitive Dual-Query Strategy with Variable-Uncertainty
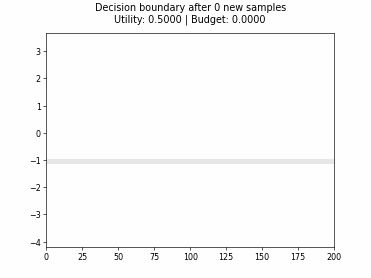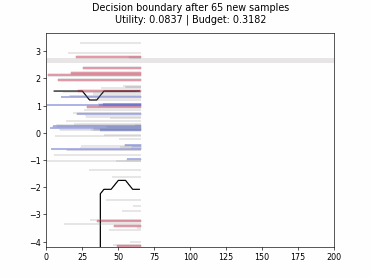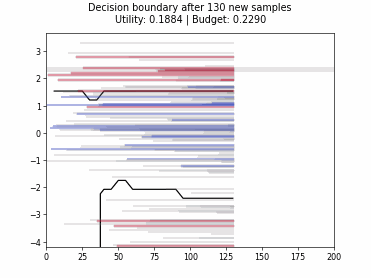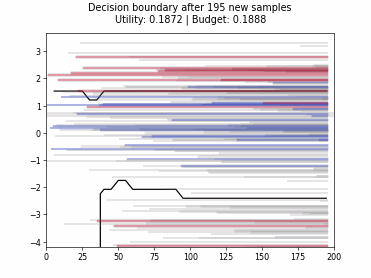
Cognitive Dual-Query Strategy with Randomized-Variable-Uncertainty
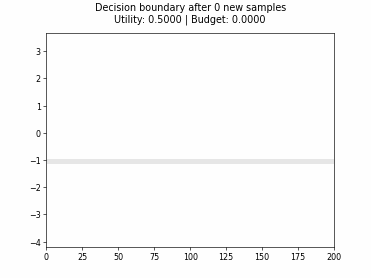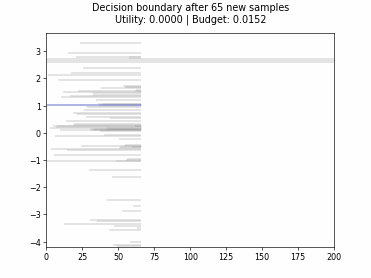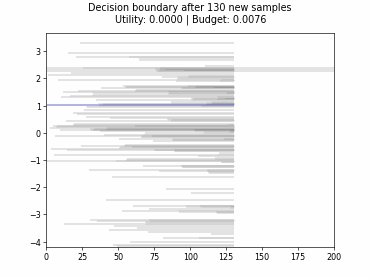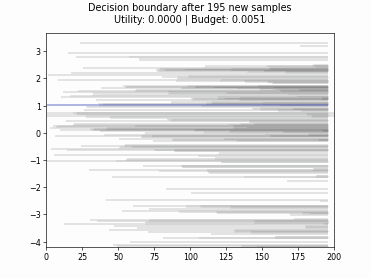
Cognitive Dual-Query Strategy with Fixed-Uncertainty