Advanced Active Learning for Regression Tasks#
Google Colab Note: If the notebook fails to run after installing the needed packages, try to restart the runtime (Ctrl + M) under Runtime -> Restart session.
[ ]:
#!pip install scikit-activeml[opt] torch torchvision xgboost
This tutorial demonstrates how to perform pool-based active learning for regression and compare query strategies using two model families:
a multilayer perceptron (MLP) trained via skorch (
torchunder the hood),a tree-boosting regressor from xgboost,
a random forest regressor from sklearn.
[2]:
# Comment in for speed up, if you have cuML installed.
# %load_ext cuml.accel
import matplotlib as mlp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import torch
import warnings
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_openml
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from skorch.toy import MLPModule
from skactiveml.pool import (
RandomSampling,
GreedySamplingTarget,
SubSamplingWrapper,
)
from skactiveml.regressor import SkorchRegressor, SklearnRegressor
from skactiveml.utils import MISSING_LABEL, call_func
from skorch.callbacks import LRScheduler
from torch import nn
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import CosineAnnealingLR
from tqdm import tqdm
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
CACHE_PATH = ".cache"
os.makedirs(CACHE_PATH, exist_ok=True)
mlp.rcParams["figure.facecolor"] = "white"
DEVICE = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
cuML: Accelerator installed.
Load Dataset#
We use our the fetch_openml function from sklearn.datasets to load the superconduct dataset from OpenML. The dataset contains information about superconductors, for which the critical temperature as a continuous target is to predicted.
[3]:
# Load and cache dataset.
X_full, y_full = fetch_openml(
data_id=43174, return_X_y=True, data_home=CACHE_PATH
)
X_full = X_full.values
y_full = y_full.values
n_features = X_full.shape[1]
# Create 80-20 train-test split.
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X_full, y_full, test_size=0.2
)
# Standardize numerical features.
sc = StandardScaler().fit(X_train)
X_train = sc.transform(X_train)
X_test = sc.transform(X_test)
Create Regression Models#
We create a dictionary of functions that can be used to create the regression models with varying seeds.
[4]:
# Setup dictionary of functions for creating regression models.
regressor_dict = {}
# Create random forest regressor.
regressor_dict["RF"] = lambda seed: SklearnRegressor(
RandomForestRegressor(random_state=seed), random_state=seed
)
# Add gradient-boosted decision tree.
regressor_dict["XGB"] = lambda seed: SklearnRegressor(
XGBRegressor(device=DEVICE, random_state=seed), random_state=seed
)
regressor_dict["MLP"] = lambda seed: SkorchRegressor(
module=MLPModule,
criterion=nn.HuberLoss,
neural_net_param_dict={
# Module-related parameters.
"module__input_units": n_features,
"module__output_units": 1,
"module__hidden_units": 256,
"module__num_hidden": 2,
"module__dropout": 0.1,
# Optimizer-related parameters.
"max_epochs": 100,
"batch_size": 128,
"optimizer": torch.optim.RAdam,
"optimizer__lr": 1e-2,
"callbacks": [
("lr_scheduler", LRScheduler(policy=CosineAnnealingLR, T_max=100))
],
# General parameters.
"verbose": 0,
"device": DEVICE,
"train_split": False,
"iterator_train__shuffle": True,
"torch_load_kwargs": {"weights_only": True},
},
sample_dtype=np.float32,
missing_label=MISSING_LABEL,
random_state=seed,
)
Create Query Strategies#
For simplicity, we only test two query strategies, of which GreedySamplingI is a dedicated strategy for regression tasks. If other strategies are to be included, we refer to our overview of query strategies.
[5]:
query_strategy_dict = {
"RandomSampling": lambda seed: RandomSampling(random_state=seed),
"GreedySamplingI": lambda seed: GreedySamplingTarget(
method="GSi", random_state=seed
),
}
Perform Active Learning Cycle#
Each active learning expirment starts with zero labels and covers 30 cycles with an acquisition batch size of 128.
[6]:
n_reps = 3
n_cycles = 30
query_batch_size = 128
n_sub_set = 1000
results = {}
for reg_name in regressor_dict:
print(reg_name)
for qs_name in query_strategy_dict:
r2_scores = np.full((n_reps, n_cycles), np.nan)
for i_rep in range(n_reps):
y = np.full_like(y_train, fill_value=MISSING_LABEL)
reg = regressor_dict[reg_name](i_rep)
qs = SubSamplingWrapper(
query_strategy_dict[qs_name](i_rep),
max_candidates=n_sub_set,
exclude_non_subsample=True,
random_state=i_rep,
)
reg.fit(X_train, y)
for c in tqdm(
range(n_cycles), desc=f"Repeat {i_rep + 1} with {qs_name}"
):
query_idx = call_func(
qs.query,
X=X_train,
y=y,
batch_size=query_batch_size,
reg=reg,
fit_reg=False,
)
y[query_idx] = y_train[query_idx]
reg.fit(X_train, y)
score = reg.score(X_test, y_test)
r2_scores[i_rep, c] = score
results[f"{reg_name}-{qs_name}"] = r2_scores
RF
Repeat 1 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:08<00:00, 3.41it/s]
Repeat 2 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:08<00:00, 3.34it/s]
Repeat 3 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:09<00:00, 3.32it/s]
Repeat 1 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:24<00:00, 1.22it/s]
Repeat 2 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:25<00:00, 1.18it/s]
Repeat 3 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:24<00:00, 1.21it/s]
XGB
Repeat 1 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:04<00:00, 6.00it/s]
Repeat 2 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:04<00:00, 6.08it/s]
Repeat 3 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:04<00:00, 6.03it/s]
Repeat 1 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:21<00:00, 1.40it/s]
Repeat 2 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:20<00:00, 1.48it/s]
Repeat 3 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [00:21<00:00, 1.42it/s]
MLP
Repeat 1 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [01:03<00:00, 2.10s/it]
Repeat 2 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [01:00<00:00, 2.02s/it]
Repeat 3 with RandomSampling: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [01:00<00:00, 2.02s/it]
Repeat 1 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [01:16<00:00, 2.54s/it]
Repeat 2 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [01:16<00:00, 2.54s/it]
Repeat 3 with GreedySamplingI: 100%|██████████| 30/30 [01:17<00:00, 2.58s/it]
Visualize Results#
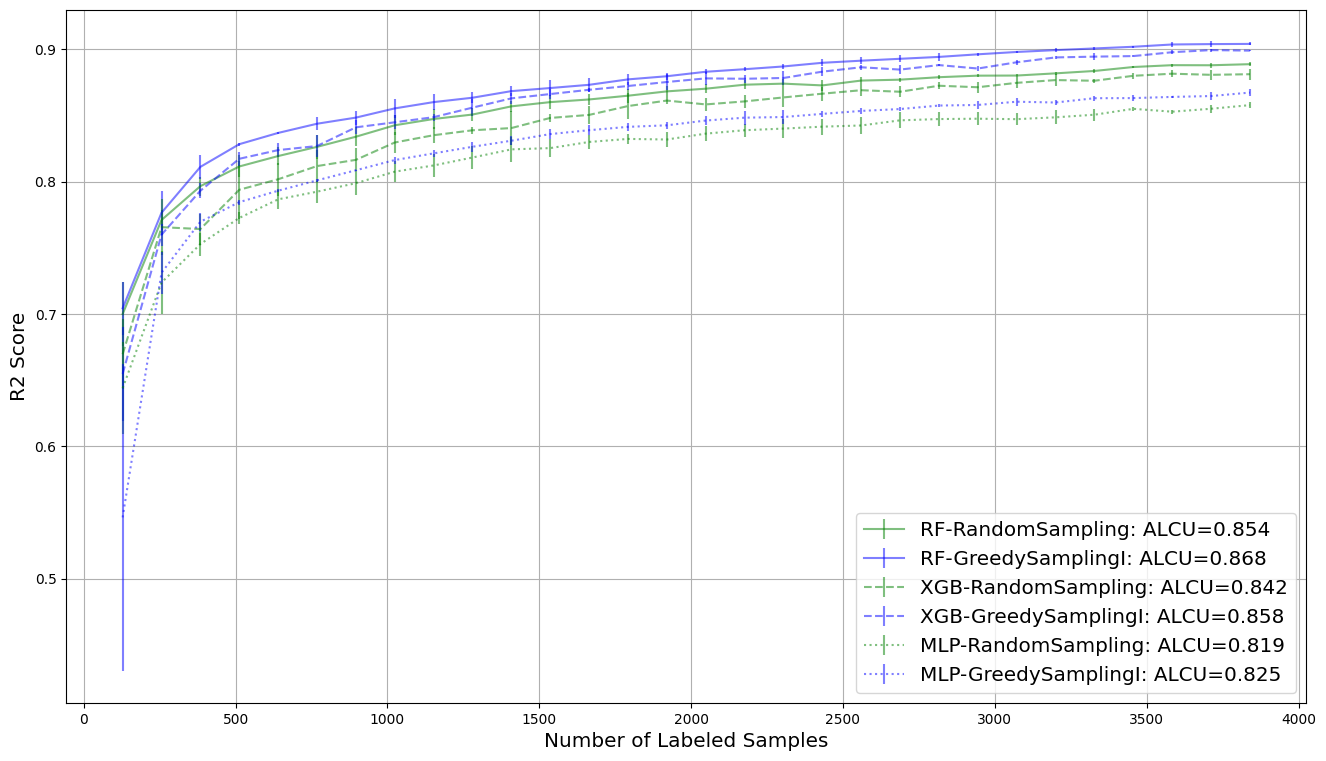
In the following, we plot the obtained learning curve of the R2 scores including the area under learning curve (AULC) score per regression model and query strategy.
[7]:
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 9))
for reg_name, ls in zip(regressor_dict, ["-", "--", ":"]):
for qs_name, c in zip(query_strategy_dict, ["g", "b"]):
key = qs_name
result = results[f"{reg_name}-{qs_name}"]
reshaped_result = result.reshape((-1, n_cycles))
errorbar_mean = np.mean(reshaped_result, axis=0)
errorbar_std = np.std(reshaped_result, axis=0)
plt.errorbar(
np.arange(1, n_cycles + 1) * query_batch_size,
errorbar_mean,
errorbar_std,
label=f"{reg_name}-{qs_name}: ALCU={np.mean(errorbar_mean):.3f}",
alpha=0.5,
color=c,
linestyle=ls,
)
plt.grid()
plt.legend(loc="lower right", fontsize="x-large")
plt.xlabel("Number of Labeled Samples", fontsize="x-large")
plt.ylabel("R2 Score", fontsize="x-large")
plt.show()