Sample Annotating#
Google Colab Note: If the notebook fails to run after installing the needed packages, try to restart the runtime (Ctrl + M) under Runtime -> Restart session.
Notebook Dependencies
Uncomment the following cells to install all dependencies for this tutorial.
[1]:
# !pip install scikit-activeml
# !pip install ipyannotations
# !pip install superintendent
# !jupyter nbextension install --user --py ipyannotations
# !jupyter nbextension enable --user --py ipyannotations
In supervised and semi-supervised machine learning it is necessary to label data after it was selected by an active learning algorithm. This tutorial shows how to make a simple annotation tool using ipyannotations and superintendent. This tutorial requires prior knowledge of our framework. If you are not familiar with it, try some basic tutorials.
NOTE: For testing execute this notebook on your local machine.
[2]:
import numpy as np
import math
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.neural_network import MLPClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from skactiveml.utils import is_labeled
from skactiveml.classifier import SklearnClassifier
from skactiveml.pool import UncertaintySampling
from superintendent import Superintendent
from ipywidgets import widgets
from ipyannotations.images import ClassLabeller
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
The Annotation Widget Class#
At first we define the class DataLabeler, which inherits from Superintendent. To adapt it to our framework, we have to overwrite the constructor and the methods _annotation_iterator, retrain, and _undo.
[3]:
from skactiveml.utils import unlabeled_indices, call_func
class DataLabeler(Superintendent):
"""DataLabeler
This class creates a widget for label assignments.
Parameters
----------
X : array-like of shape (n_samples, *)
Training data set, usually complete, i.e. including the labeled and
unlabeled samples.
y : array-like of shape (n_samples,)
Labels of the training data set (possibly including unlabeled ones
indicated by self.MISSING_LABEL).
clf : skactiveml.base.SkactivemlClassifier
Model implementing the method `fit`. Check `query_strategy` for
compatibility.
query_strategy : skactiveml.base.QueryStrategy
Query strategy used to select the next sample(s) to be labeled.
labelling_widget : Optional (widgets.Widget)
An input widget. This needs to follow the interface of the class
`superintendent.controls.base.SubmissionWidgetMixin`.
query_dict : dict, default=None
A dictionary with additional arguments past to `query_strategy`.
shape_query : Tuple, default=None
The shape of `X` that is expected of `query_strategy`.
shape_clf : tuple, default=None
The shape of `X` that is expected of `clf.fit`.
batch_size : int, default=1
The number of samples to be selected in one AL cycle.
n_cycles : int, default=None
`n_cycles`*`batch_size` is the maximum number of samples you want to
annotate. If `None`, the entire dataset is requested for labeling.
X_eval : array-like of shape (n_eval_samples, n_features), default=None
Evaluation data set that is used by the `eval_method`. Only used if
`y_eval` is specified.
y_eval : array-like of shape (n_eval_samples), default=None
Labels for the evaluation data set. Only used if `X_eval` is
specified.
clf_eval : skactiveml.base.SkactivemlClassifier
Model implementing the method `fit`, passed to the `eval_method`.
If None, `clf` is used.
eval_method : callable
A function that accepts three arguments - `clf`, `X`, and `y` - and
returns a validation score of the `clf`. If None,
`sklearn.model_selection.cross_val_score` is used.
"""
def __init__(
self,
X,
y,
clf,
query_strategy,
labelling_widget,
query_dict=None,
shape_query=None,
shape_clf=None,
batch_size=1,
n_cycles=None,
X_eval=None,
y_eval=None,
clf_eval=None,
eval_method=None,
**kwargs,
):
# Call the super constructor.
try:
super().__init__(
labelling_widget=labelling_widget,
eval_method=eval_method,
**kwargs
)
except AttributeError:
pass
# Assign parameters.
self.X = X
self.y = y
self.clf = clf
self.shape_query = shape_query
self.shape_clf = shape_clf
self.X_eval = X_eval
self.y_eval = y_eval
self.clf_eval = clf_eval or clf
self.query_dict = query_dict or {}
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.query_strategy = query_strategy
self.n_cycles = n_cycles or math.ceil(len(X)/batch_size)
self.labeled_indices = []
self.labels = []
self.candidates = unlabeled_indices(y)
# Generate the widgets.
self.model_performance = widgets.HTML(value="")
self.top_bar = widgets.HBox(
[
widgets.HBox(
[self.progressbar],
layout=widgets.Layout(width="50%",
justify_content="space-between"),
),
widgets.HBox(
[self.model_performance],
layout=widgets.Layout(width="50%"),
),
]
)
self.children = [self.top_bar, self.labelling_widget]
# Start the annotation loop.
self._begin_annotation()
def _annotation_iterator(self):
"""The annotation loop."""
self.children = [self.top_bar, self.labelling_widget]
self.progressbar.bar_style = ""
# Fit the clf
self.retrain()
i = 0
y = None
while i < self.n_cycles:
# Query the next batch of samples.
self.query_dict["X"] = self.X.reshape(self.shape_query)
idx = call_func(self.query_strategy.query,
y=self.y,
clf=self.clf,
reg=self.clf,
ensemble=self.clf,
candidates=self.candidates,
batch_size=self.batch_size,
**self.query_dict)
j = 0
if y == 'undo':
j = self.batch_size-1
if self.batch_size != 1:
self.y[self.labeled_indices[-j:]] = self.labels[-j:]
self.candidates = np.delete(
self.candidates,
self.labeled_indices[-j:]
)
while j<len(idx):
# Display and label the next sample.
with self._render_hold_message("Loading..."):
self.labelling_widget.display(self.X[idx[j]])
y = yield
if y is None:
y = self.clf.missing_label
if y == 'undo':
# If the undo button is press, the previous step is undone.
if j==0:
i -= 2
self.y[self.labeled_indices[-self.batch_size:]] = \
self.clf.missing_label
self.candidates = np.sort(np.append(
self.candidates,
self.labeled_indices[-self.batch_size:]
))
self.labels.pop()
self.labeled_indices.pop()
self.progressbar.value = \
np.sum(is_labeled(self.y))\
/(min(self.n_cycles*self.batch_size, len(self.X)))
break
self.y[self.labeled_indices[-1]] = self.clf.missing_label
self.labels.pop()
self.candidates = np.append(
self.candidates, self.labeled_indices.pop()
)
j -= 2
else:
# Assigning the label.
self.labeled_indices.append(idx[j])
self.labels.append(y)
self.y[idx[j]] = y
self.candidates = self.candidates[self.candidates!=idx[j]]
self.progressbar.value = \
((j+i*self.batch_size)
/(min(self.n_cycles*self.batch_size, len(self.X))))
j += 1
# Fit the clf.
self.retrain()
# Brake if all samples are labeled.
if len(self.candidates) == 0:
break
i += 1
yield self._render_finished()
def _undo(self):
if len(self.labeled_indices) > 0:
self._annotation_loop.send('undo') # Advance next item
def retrain(self, button=None):
"""Re-train the `clf` you passed when creating this widget.
This calls the `fit` method of your `clf` with the data that you've
labeled. It will also score the classifier and display the
performance.
Parameters
----------
button : widget.Widget, optional
Optional & ignored; this is passed when invoked by a button.
"""
with self._render_hold_message("Retraining..."):
if self.X_eval is not None:
X_eval = self.X_eval
y_eval = self.y_eval
else:
X_eval = self.X[is_labeled(self.y)]
y_eval = self.y[is_labeled(self.y)]
shape_clf = (len(X_eval), *self.shape_clf[1:])
# Fit the clf.
try:
self.clf.fit(self.X.reshape(self.shape_clf), self.y)
except ValueError as e:
if str(e).startswith(
"This solver needs samples of at least 2"
):
self.model_performance.value = \
"Not enough classes to retrain."
return
else:
raise
# Evaluate the clf. By default, using cross validation.
# In sklearn this clones the clf, so it's OK to do after the clf
# fit.
try:
if self.eval_method is not None:
performance = np.mean(
self.eval_method(
self.clf_eval,
X_eval.reshape(shape_clf),
y_eval
)
)
else:
performance = np.mean(
cross_val_score(
self.clf_eval,
X_eval.reshape(shape_clf),
y_eval,
cv=3,
error_score=np.nan
)
)
except ValueError as e:
if "n_splits=" in str(e) \
or "Found array with 0 sample(s)" in str(e) \
or "cannot reshape array of size 0" in str(e):
self.model_performance.value = \
"Not enough labels to evaluate."
return
else:
raise
self.model_performance.value = f"Score: {performance:.3f}"
Create Dataset#
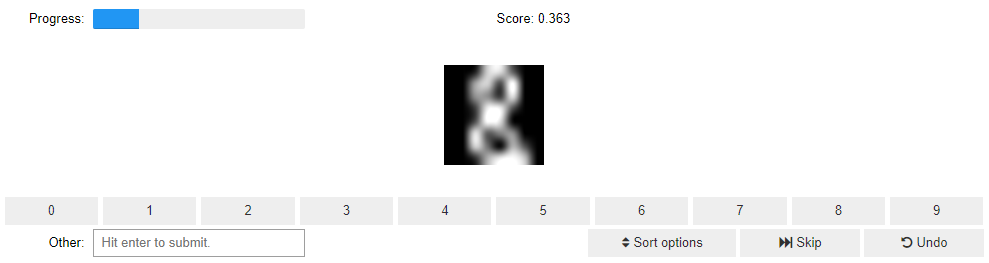
For this tutorial we use the digit data set available through the sklearn package. The 8x8 images show handwritten digits from 0 to 9.
[4]:
X = load_digits().data.reshape(-1, 8, 8)
y = np.full(shape=len(X), fill_value=np.nan)
Create and Start Annotation Process#
As classifier, MLPClassifier and StandardScaler by sklearn is used in a pipeline and UncertaintySampling from our framework Skactiveml as query strategy. ClassLabeller creates a ipywidget, which displays the selected sample and provides the labelling interface for the user. This class can be exchanged by other widgets to support different types of data. The DataLabeler-widget manages the iteration
over the data set.
[5]:
random_state = 42
pipe = Pipeline([('scaler', StandardScaler()), ('MLP', MLPClassifier(random_state=random_state))])
clf = SklearnClassifier(pipe, classes=range(10), random_state=random_state)
qs = UncertaintySampling(random_state=random_state)
labelling_widget = ClassLabeller(
options=list(range(0, 10)), image_size=(100, 100)
)
data_labeler = DataLabeler(
X=X,
y=y,
clf=clf,
shape_query=(len(X), -1),
shape_clf=(len(X), -1),
query_strategy=qs,
labelling_widget=labelling_widget,
batch_size=2,
n_cycles=50
)
data_labeler
The cell above produces an output which looks like the following image.