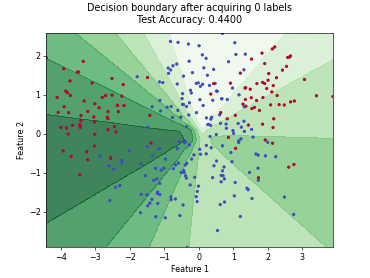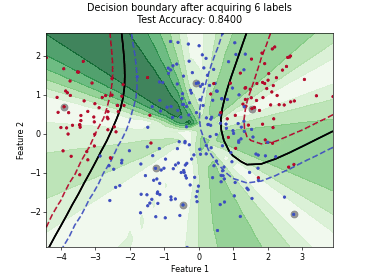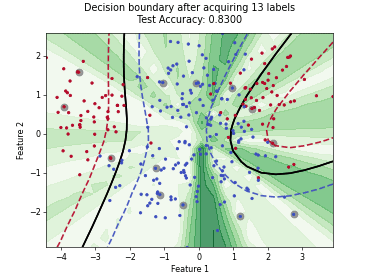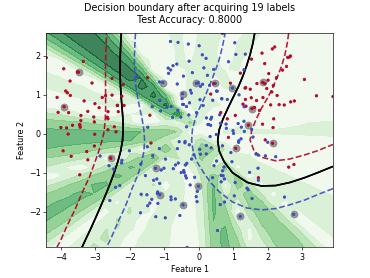
MaxHerding#
- class skactiveml.pool.MaxHerding(normalize_samples=True, metric='rbf', metric_dict=None, missing_label=nan, random_state=None)[source]#
Bases:
SingleAnnotatorPoolQueryStrategyThis class implements the MaxHerding query strategy [1], which greedily selects batch_size unlabeled samples that most increase a smooth, kernel-based coverage objective in embedding space, accounting for the already labeled set. The objective promotes representativeness and diversity via kernel similarity.
- Parameters:
- normalize_samplesbool, default=True
Flag whether to normalize the samples to have unit length.
- metricstr or callable, default=None
The metric must be None or a valid kernel as defined by the function sklearn.metrics.pairwise.pairwise_kernels.
- metric_dictdict, default=None
Any further parameters that should be passed directly to the kernel function sklearn.metrics.pairwise.pairwise_kernels.
- missing_labelscalar or string or np.nan or None, default=np.nan
Value to represent a missing label.
- random_stateNone or int or np.random.RandomState, default=None
The random state to use.
References
[1]Bae, Wonho, Junhyug Noh, and Danica J. Sutherland. “Generalized Coverage for More Robust Low-Budget Active Learning.” In Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2024.
Methods
Get metadata routing of this object.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
query(X, y[, candidates, batch_size, ...])Determines for which candidate samples labels are to be queried.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
- get_metadata_routing()#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- query(X, y, candidates=None, batch_size=1, return_utilities=False)[source]#
Determines for which candidate samples labels are to be queried.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data set, usually complete, i.e., including the labeled and unlabeled samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
Labels of the training data set (possibly including unlabeled ones indicated by self.missing_label).
- candidatesNone or array-like of shape (n_candidates,), dtype=int or array-like of shape (n_candidates, n_features), default=None
If candidates is None, the unlabeled samples from (X,y) are considered as candidates.
If candidates is of shape (n_candidates,) and of type int, candidates is considered as the indices of the samples in (X,y).
- batch_sizeint, default=1
The number of samples to be selected in one AL cycle.
- return_utilitiesbool, default=False
If True, also return the utilities based on the query strategy.
- Returns:
- query_indicesnumpy.ndarray of shape (batch_size,)
The query indices indicate for which candidate sample a label is to be queried, e.g., query_indices[0] indicates the first selected sample. The indexing refers to the samples in X.
- utilitiesnumpy.ndarray of shape (batch_size, n_samples) or numpy.ndarray of shape (batch_size, n_candidates)
The utilities of samples after each selected sample of the batch, e.g., utilities[0] indicates the utilities used for selecting the first sample (with index query_indices[0]) of the batch. Utilities for labeled samples will be set to np.nan. The indexing refers to the samples in X.
- set_params(**params)#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.