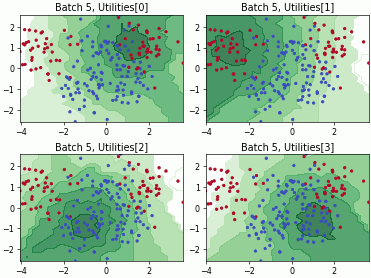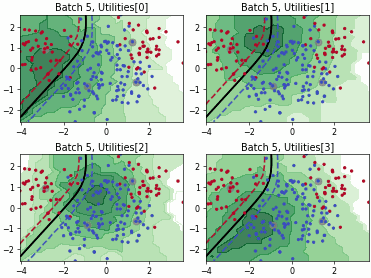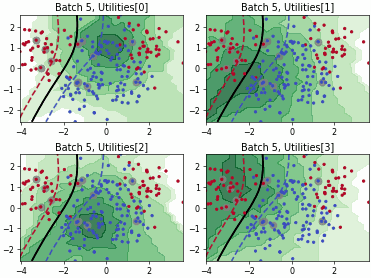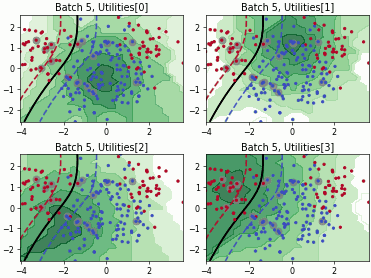
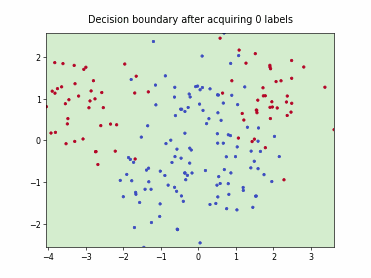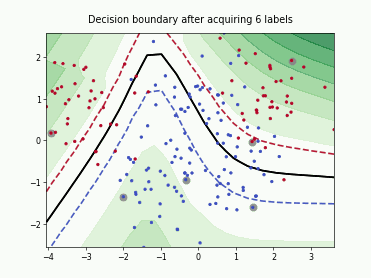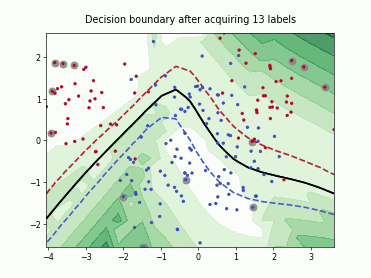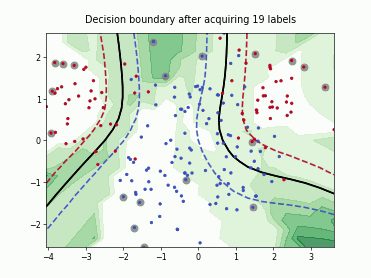
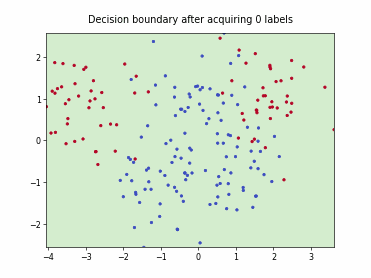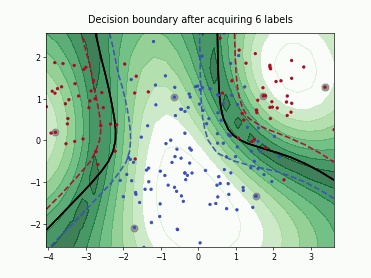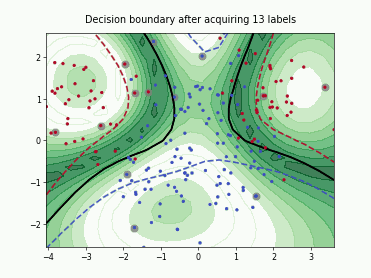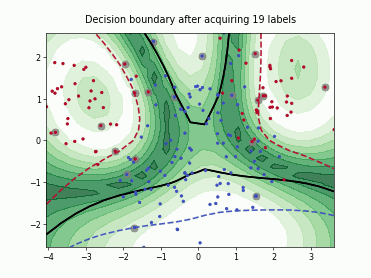
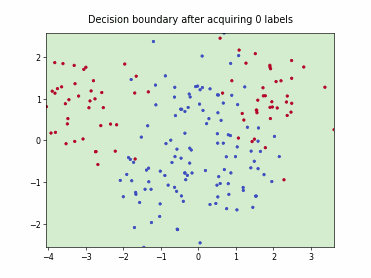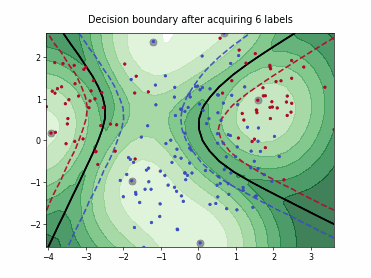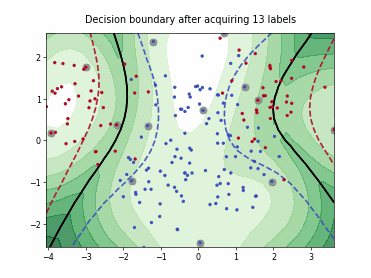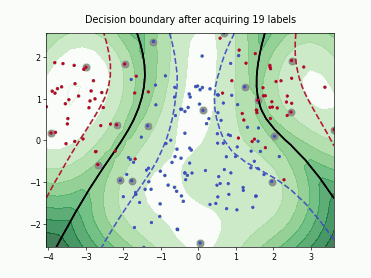
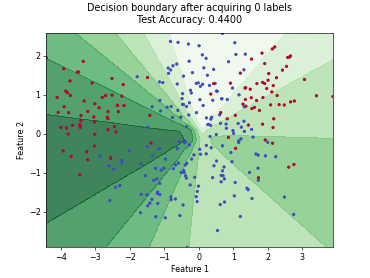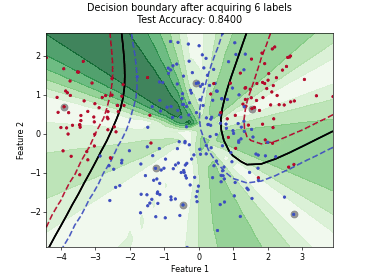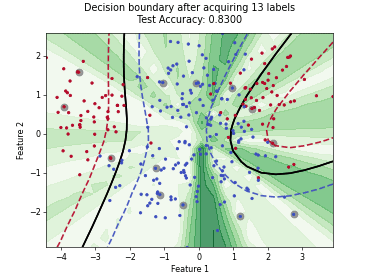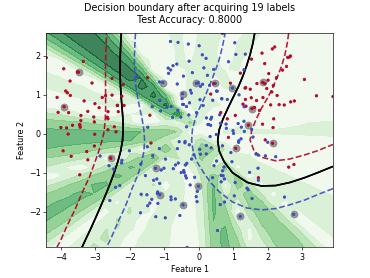
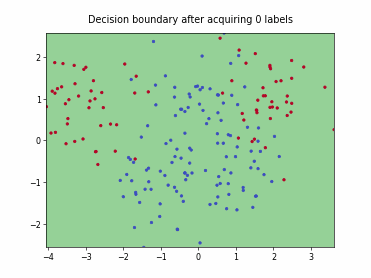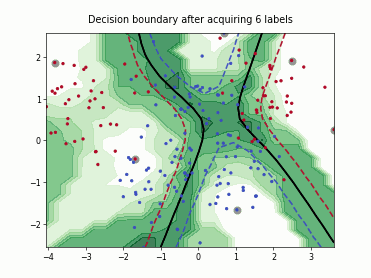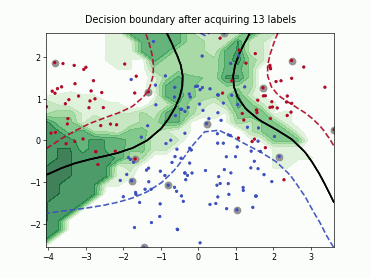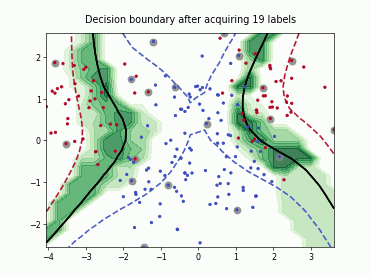
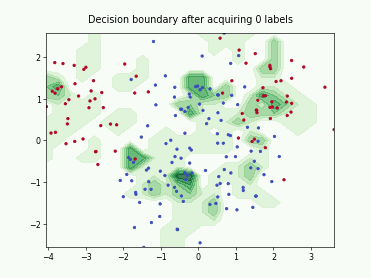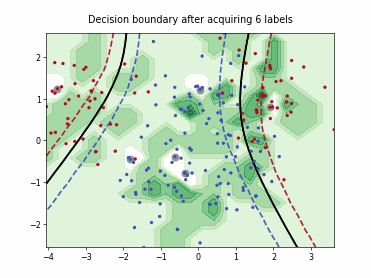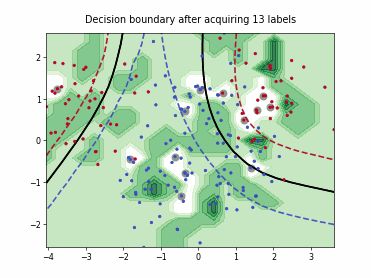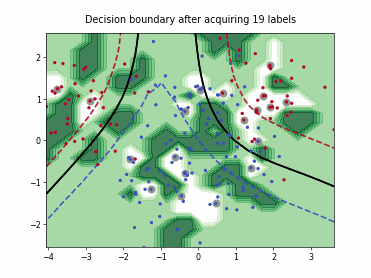
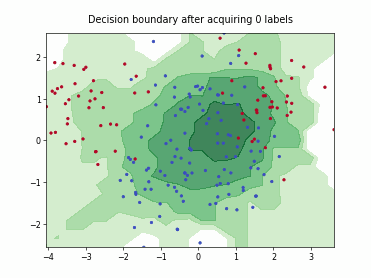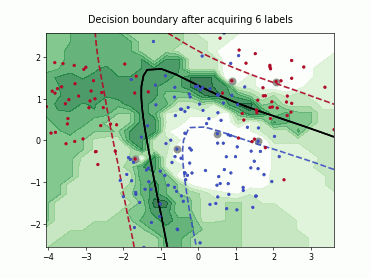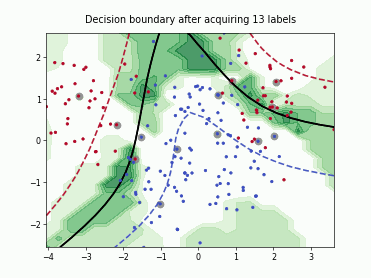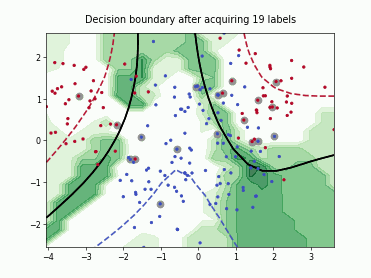
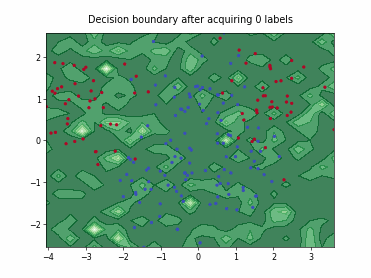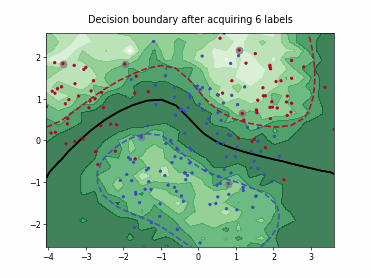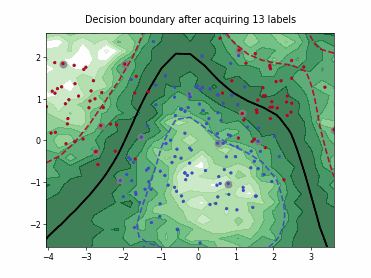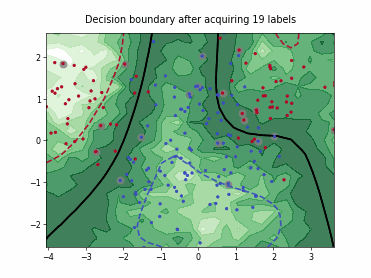
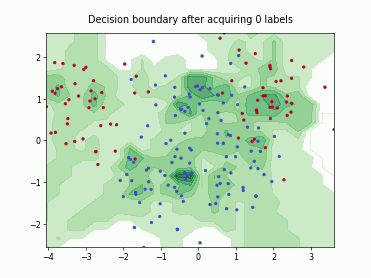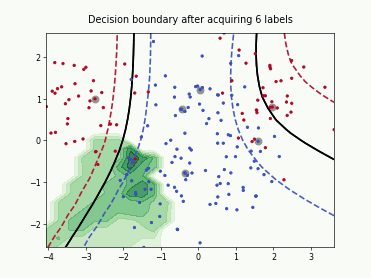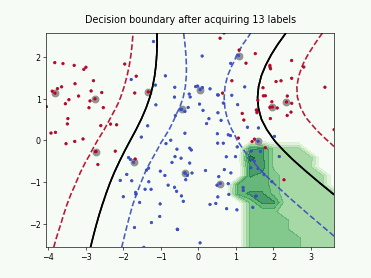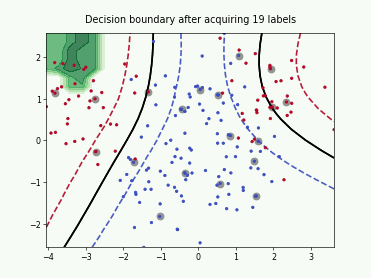
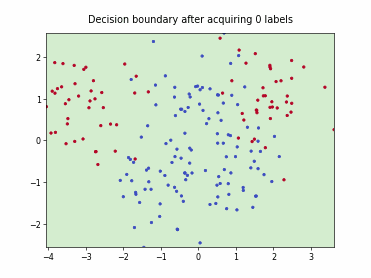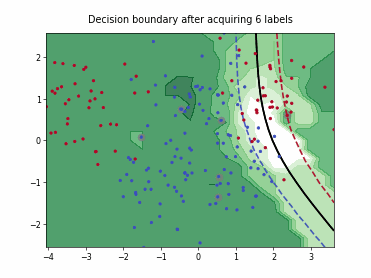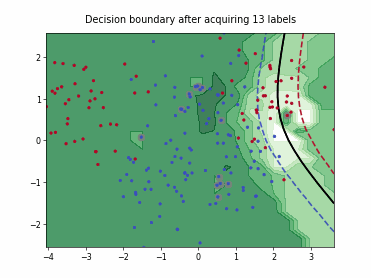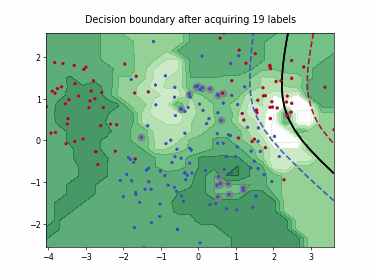
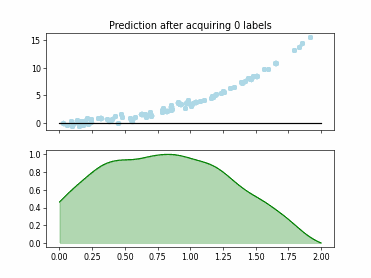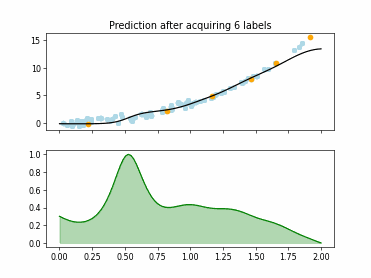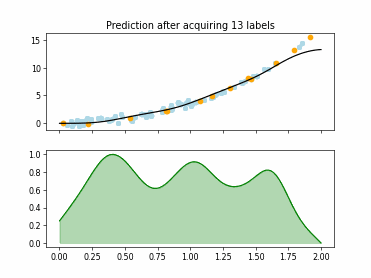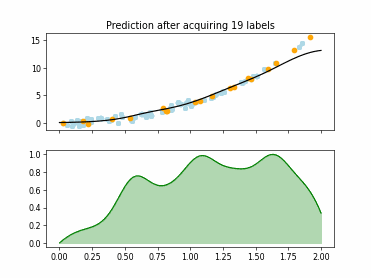
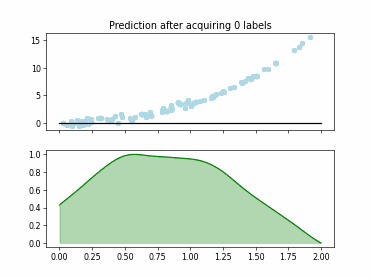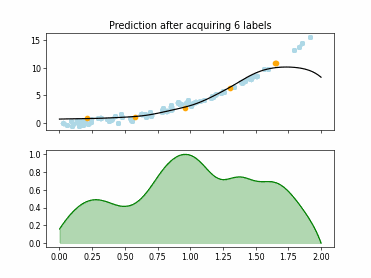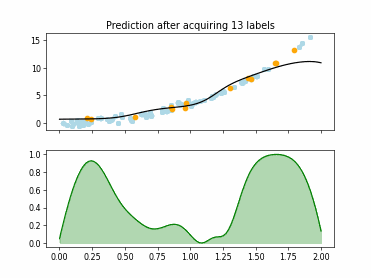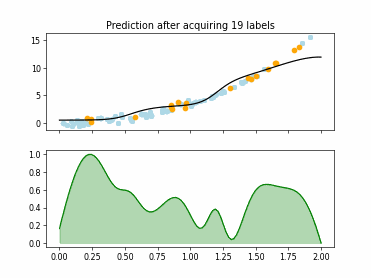
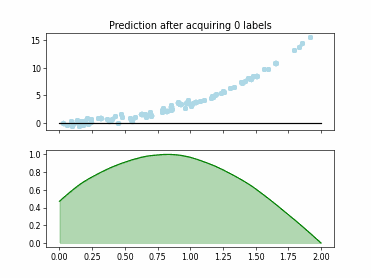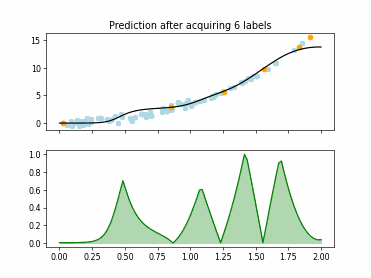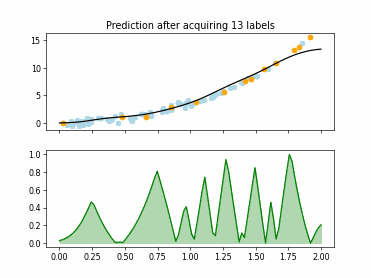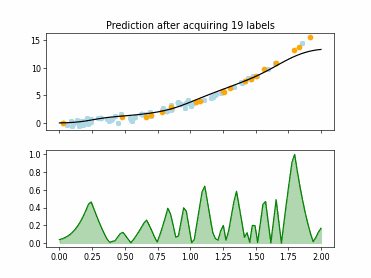
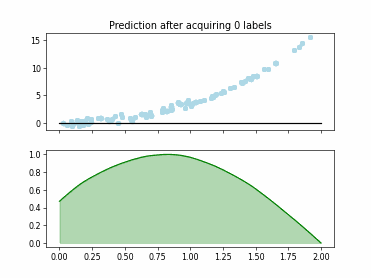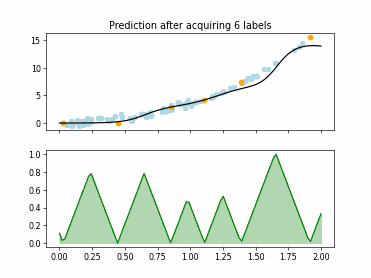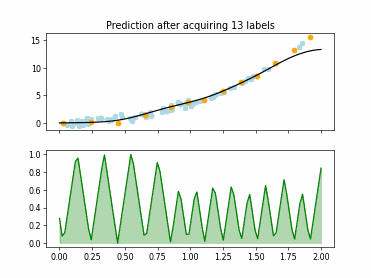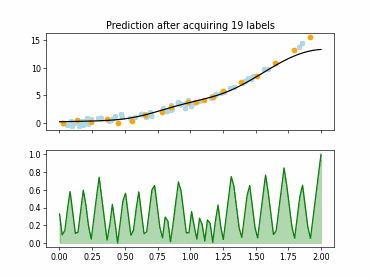
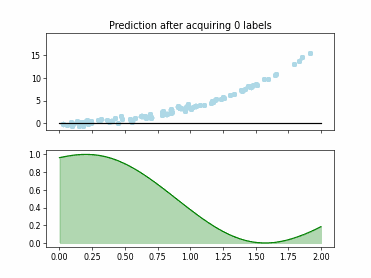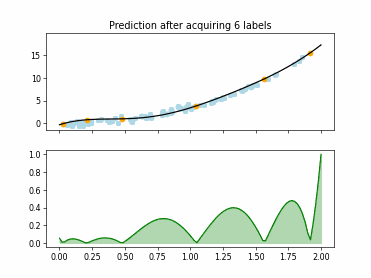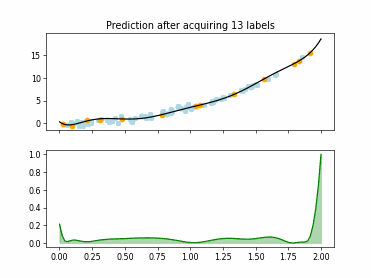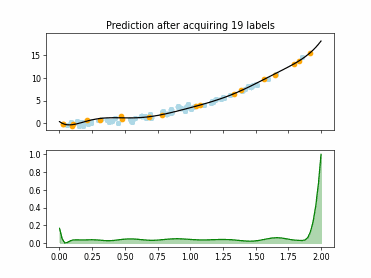
SingleAnnotatorPoolQueryStrategy#
- class skactiveml.base.SingleAnnotatorPoolQueryStrategy(missing_label=nan, random_state=None)[source]#
Bases:
PoolQueryStrategyBase class for all pool-based active learning query strategies with a single annotator in scikit-activeml.
Methods
Get metadata routing of this object.
get_params([deep])Get parameters for this estimator.
query(X, y, *args[, candidates, batch_size, ...])Determines for which candidate samples labels are to be queried.
set_params(**params)Set the parameters of this estimator.
- get_metadata_routing()#
Get metadata routing of this object.
Please check User Guide on how the routing mechanism works.
- Returns:
- routingMetadataRequest
A
MetadataRequestencapsulating routing information.
- get_params(deep=True)#
Get parameters for this estimator.
- Parameters:
- deepbool, default=True
If True, will return the parameters for this estimator and contained subobjects that are estimators.
- Returns:
- paramsdict
Parameter names mapped to their values.
- abstract query(X, y, *args, candidates=None, batch_size=1, return_utilities=False, **kwargs)[source]#
Determines for which candidate samples labels are to be queried.
- Parameters:
- Xarray-like of shape (n_samples, n_features)
Training data set, usually complete, i.e. including the labeled and unlabeled samples.
- yarray-like of shape (n_samples,)
Labels of the training data set (possibly including unlabeled ones indicated by self.missing_label).
- candidatesNone or array-like of shape (n_candidates), dtype=int or array-like of shape (n_candidates, n_features), default=None
If candidates is None, the unlabeled samples from (X,y) are considered as candidates.
If candidates is of shape (n_candidates,) and of type int, candidates is considered as the indices of the samples in (X,y).
If candidates is of shape (n_candidates, …), the candidate samples are directly given in candidates (not necessarily contained in X). This is not supported by all query strategies.
- batch_sizeint, default=1
The number of samples to be selected in one AL cycle.
- return_utilitiesbool, default=False
If true, also return the utilities based on the query strategy.
- Returns:
- query_indicesnumpy.ndarray of shape (batch_size,)
The query indices indicate for which candidate sample a label is to be queried, e.g., query_indices[0] indicates the first selected sample.
If candidates is None or of shape (n_candidates,), the indexing refers to the samples in X.
If candidates is of shape (n_candidates, n_features), the indexing refers to the samples in candidates.
- utilitiesnumpy.ndarray of shape (batch_size, n_samples) or numpy.ndarray of shape (batch_size, n_candidates)
The utilities of samples after each selected sample of the batch, e.g., utilities[0] indicates the utilities used for selecting the first sample (with index query_indices[0]) of the batch. Utilities for labeled samples will be set to np.nan.
If candidates is None or of shape (n_candidates,), the indexing refers to the samples in X.
If candidates is of shape (n_candidates, n_features), the indexing refers to the samples in candidates.
- set_params(**params)#
Set the parameters of this estimator.
The method works on simple estimators as well as on nested objects (such as
Pipeline). The latter have parameters of the form<component>__<parameter>so that it’s possible to update each component of a nested object.- Parameters:
- **paramsdict
Estimator parameters.
- Returns:
- selfestimator instance
Estimator instance.
Examples using skactiveml.base.SingleAnnotatorPoolQueryStrategy#
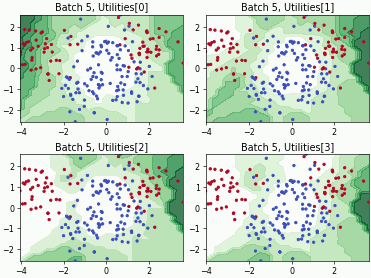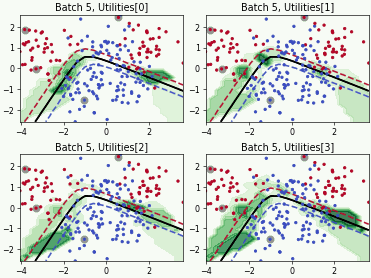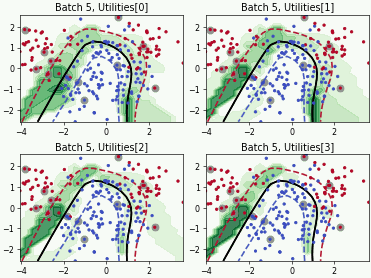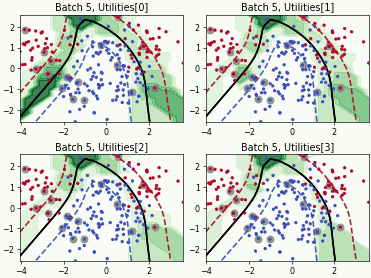
Batch Active Learning by Diverse Gradient Embedding (BADGE)
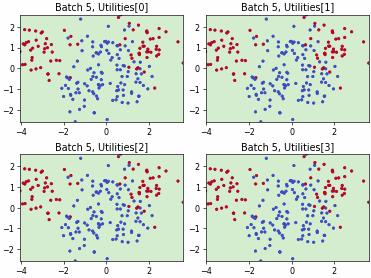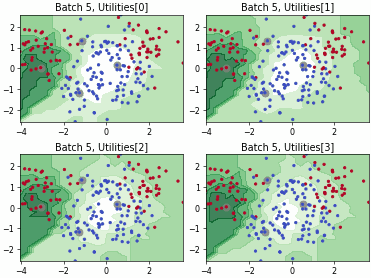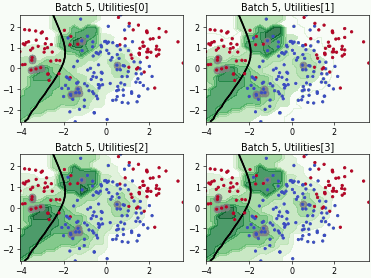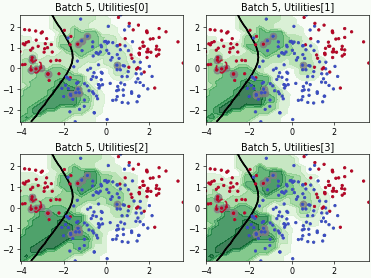
Batch Bayesian Active Learning by Disagreement (BatchBALD)
Fast Active Learning by Contrastive UNcertainty (FALCUN)
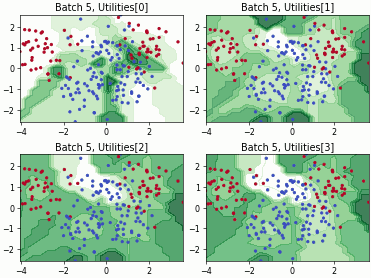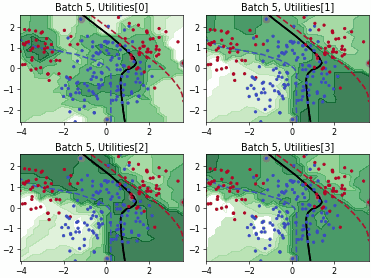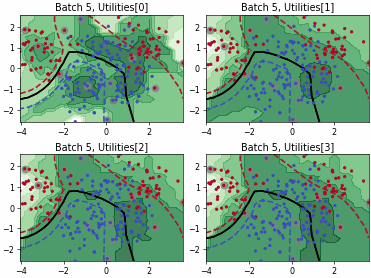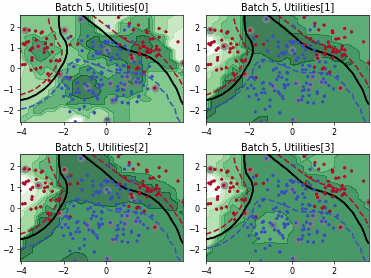
Batch Density-Diversity-Distribution-Distance Sampling (4DS)
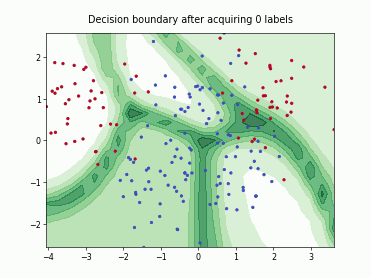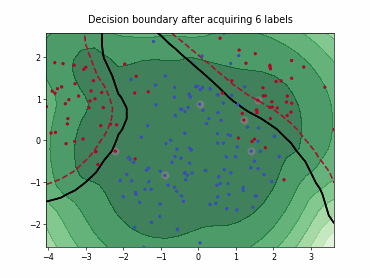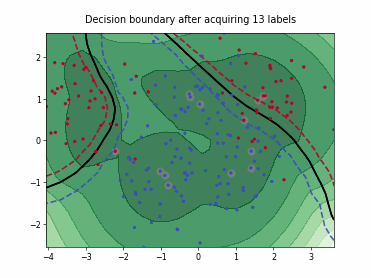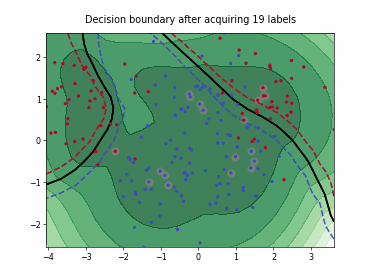
Density-Diversity-Distribution-Distance Sampling (4DS)
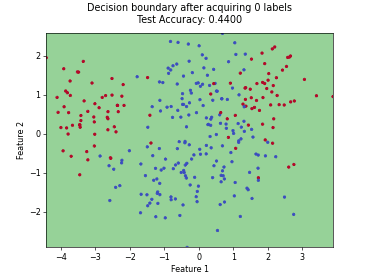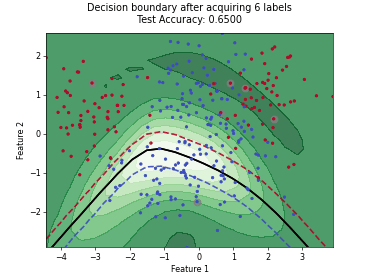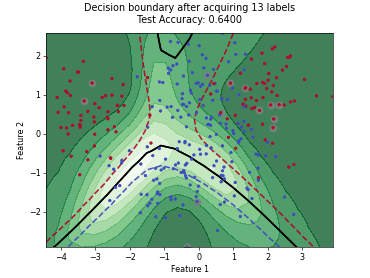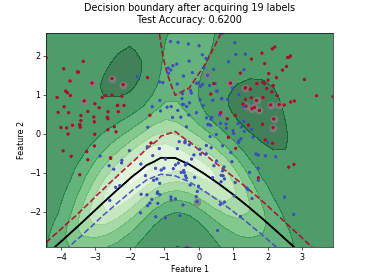
Monte-Carlo Expected Error Reduction (EER) with Log-Loss
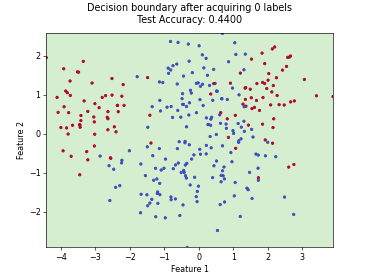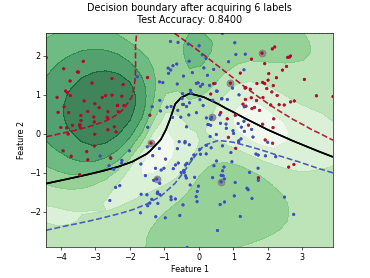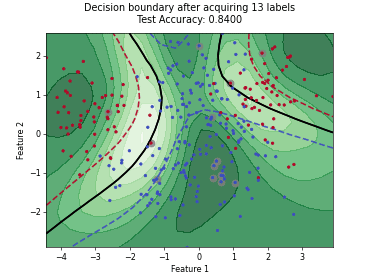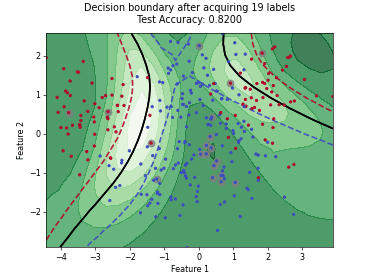
Monte-Carlo Expected Error Reduction (EER) with Misclassification-Loss
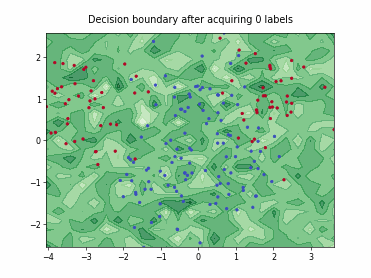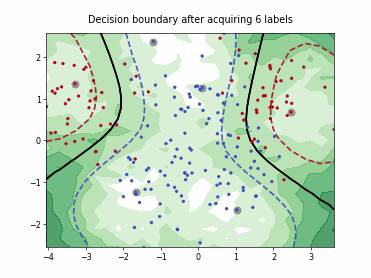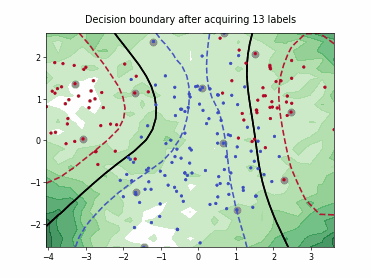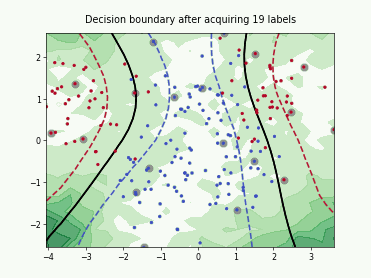
Query-by-Committee (QBC) with Kullback-Leibler Divergence
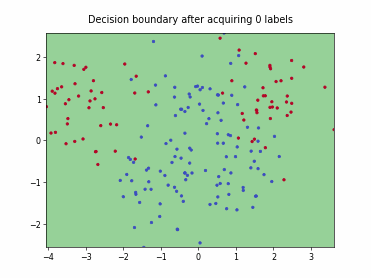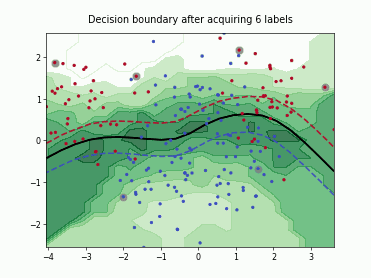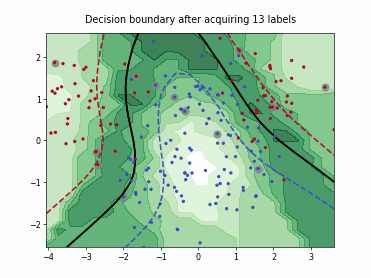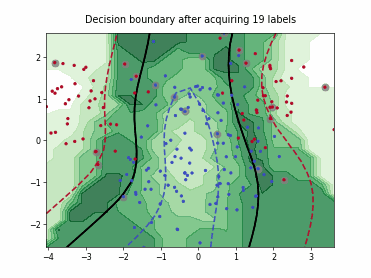
Querying Informative and Representative Examples (QUIRE)

Uncertainty Sampling with Expected Average Precision (USAP)
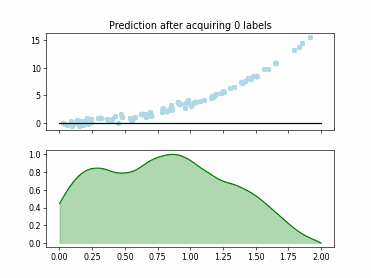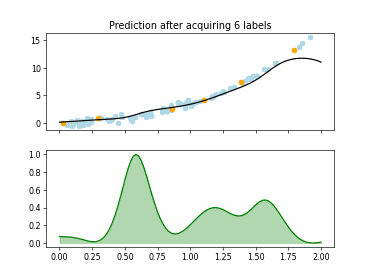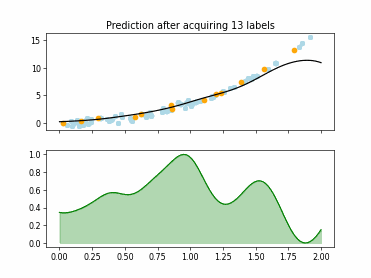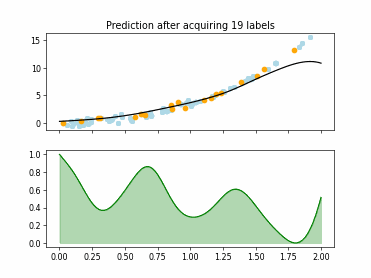
Regression based Kullback Leibler Divergence Maximization
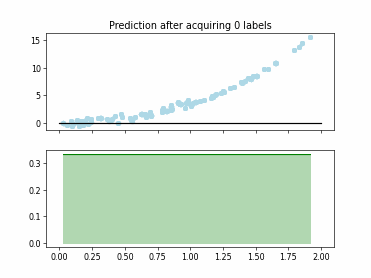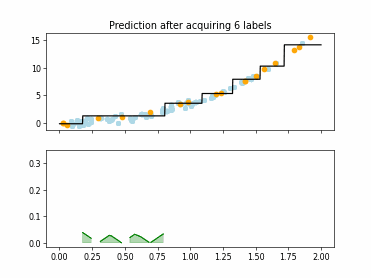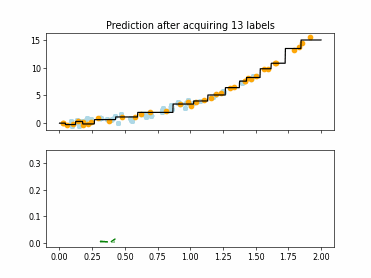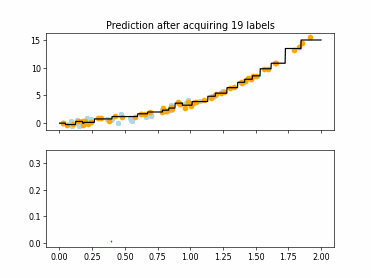
Regression Tree Based Active Learning (RT-AL) with Diversity Selection
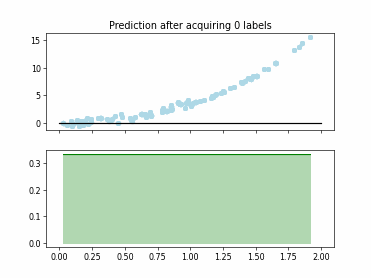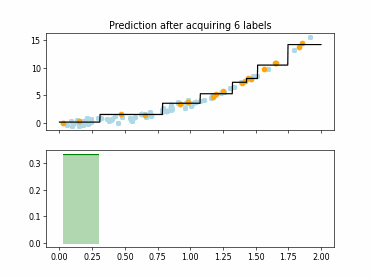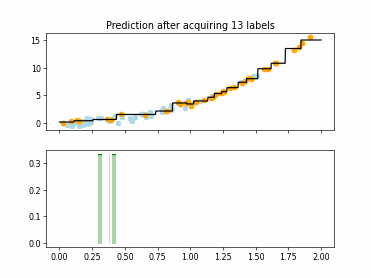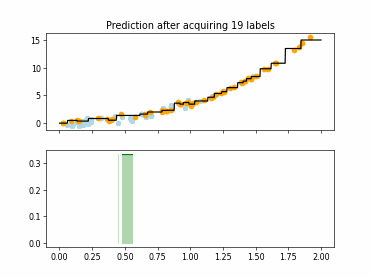
Regression Tree Based Active Learning (RT-AL) with Random Selection
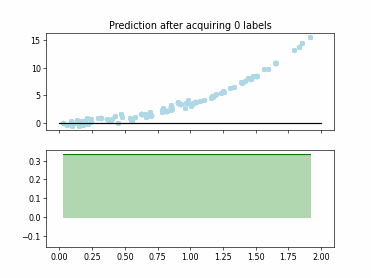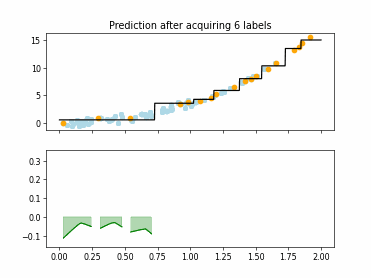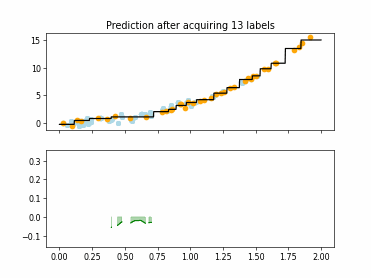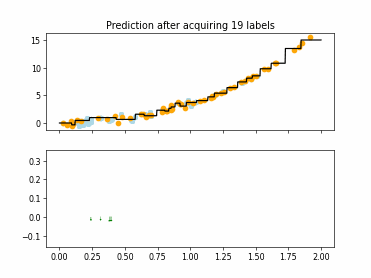
Regression Tree Based Active Learning (RT-AL) with Representativity Selection